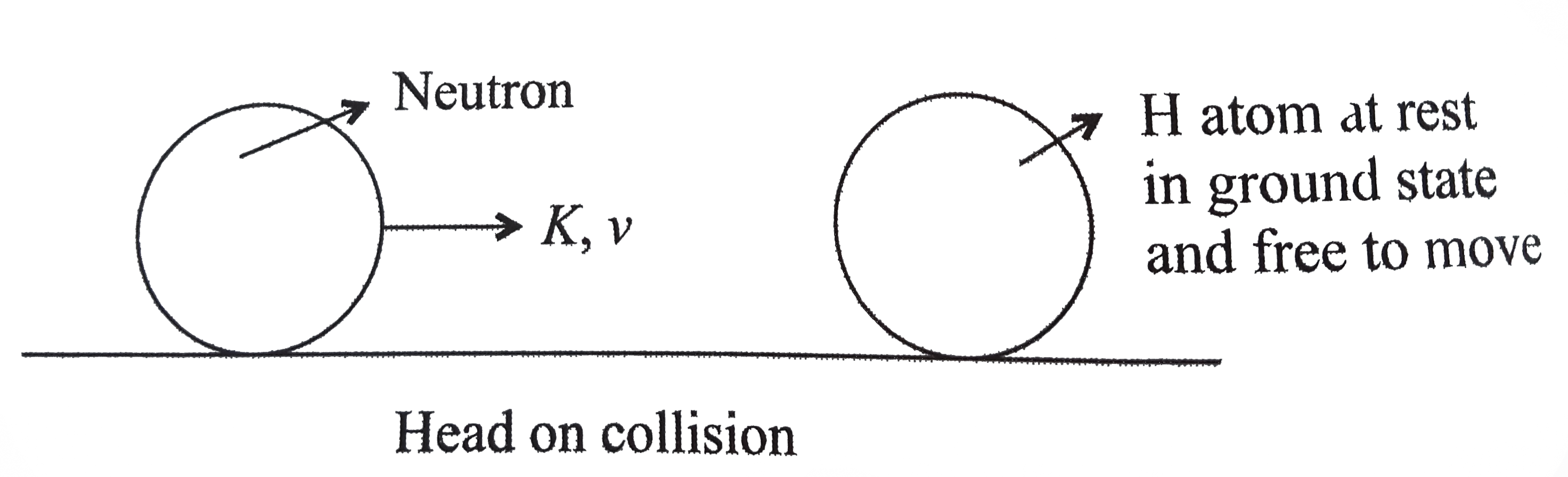Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the figure , what type of collision can be possible , if K = 14 eV,...
Text Solution
|
- A photon collides with a stationary hydrogen atom in ground state inel...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure , what type of collision can be possible , if K = 14 eV,...
Text Solution
|
- For a perfectly elastic collision and a perfectly inelastic collision,...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron collides with a stationary He + atom in its ground state, Wh...
Text Solution
|
- Elastic , Inelastic and Perfectly inelastic collions
Text Solution
|
- Explain the elastic and inelastic types of collisions.
Text Solution
|
- The work function for AI, K and Pt is 4.28 eV, 2.30 eV and 5.65 eV res...
Text Solution
|
- A photon collides with a stationary hydrogen atom in ground state inel...
Text Solution
|