Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY ENGLISH-PROJECTILE MOTION-Level - 2 Subjective
- Determine the horizontal velocity v0 with which a stone must be projec...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is dropped from point P at time t = 0. At the same time an...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles are simultaneously projected in the same vertical plane ...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile takes off with an initial velocity of 10 m//s at an angle...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from the ground in such a direction so as to hit ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is released from a certain height H = 400m. Due to the wind...
Text Solution
|
- A train is moving with a constant speed of 10m//s in a circle of radiu...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected from an inclined plane OP1 from A with velocit...
Text Solution
|
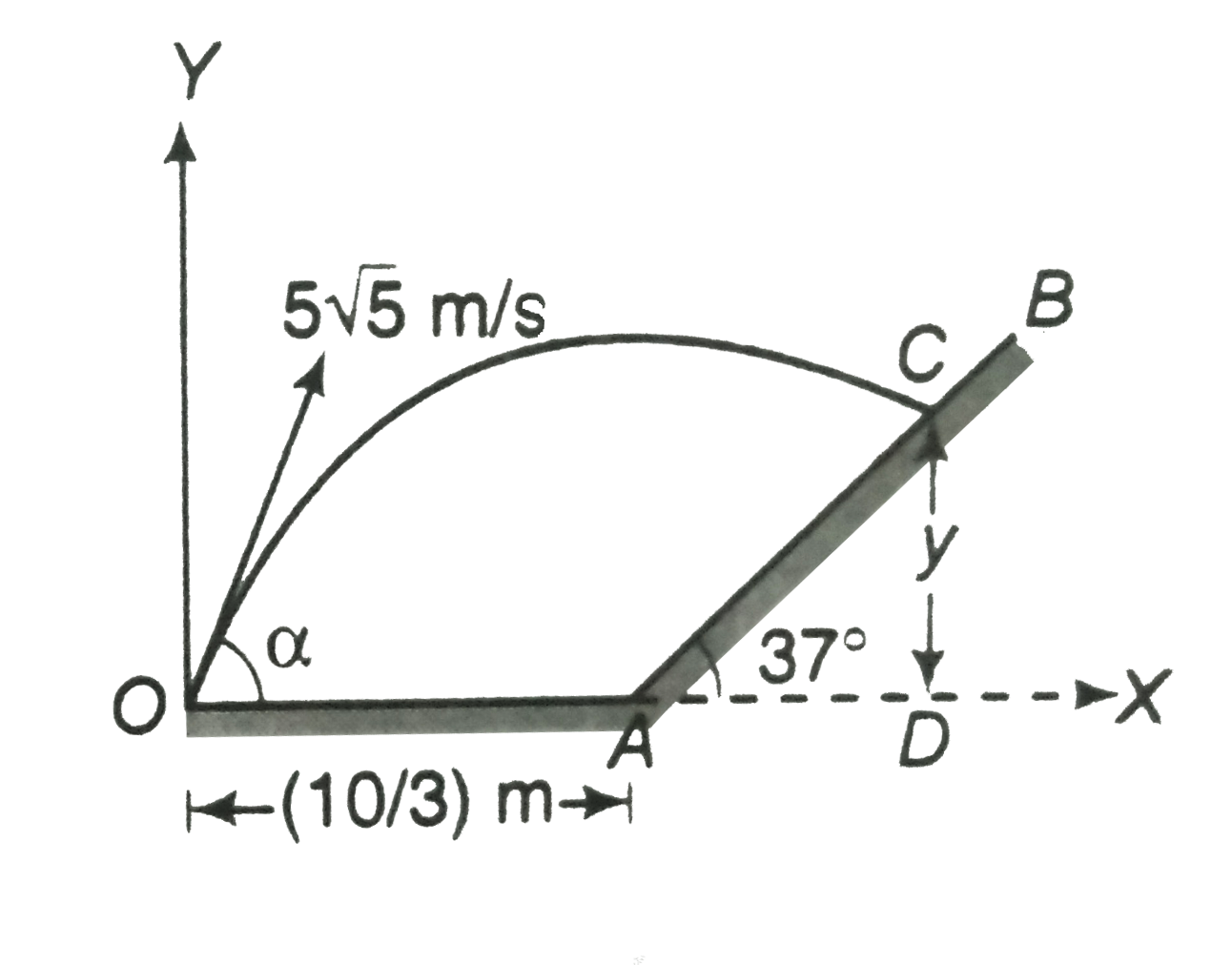
- A particle is projected from point O on the ground with velocity u = 5...
Text Solution
|
- A plank fitted with a gun is moving on a horizontal surface with speed...
Text Solution
|