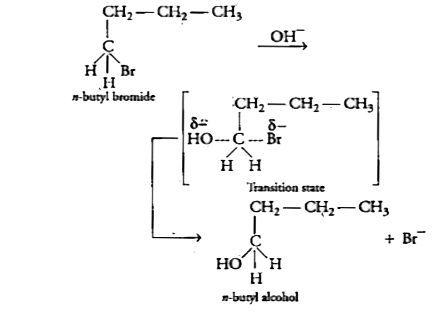
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES (ALKYL HALIDE)
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise PART-II- QUESTION FOR PRACTICE (SHORT ANSWER TYPE II QUESTIONS)|27 VideosHALOALKANES (ALKYL HALIDE)
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise PART-II- QUESTION FOR PRACTICE (LONG ANSWER TYPE II QUESTIONS)|12 VideosHALOALKANES (ALKYL HALIDE)
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise PART-II- QUESTION FOR PRACTICE (VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|9 VideosGROUP 18 ELEMENTS NOBLEGASES
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE ( Long Answer Type Questions )|6 VideosPHENOLS
ARIHANT PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE (Long Answer Type Questions )|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES (ALKYL HALIDE) -PART-II- QUESTION FOR PRACTICE (SHORT ANSWER TYPE I QUESTIONS)
- Why alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water?
Text Solution
|
- Why is the solubility of haloalkanes in water very low?
Text Solution
|
- Arrange each set of compounds in the order of increasing boiling point...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange each set of compounds in the order of increasing boiling point...
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of the following reaction: nBuBr+KCNoverset(EtOH...
Text Solution
|
- In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes ...
Text Solution
|
- Which alkyl halide from the following pair is chiral and undergoes fas...
Text Solution
|
- Out of S(N)1 and S(N)2 which reaction occurs with (a) inversion of c...
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in S(N...
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in S(N...
Text Solution
|
- Tert-butylbromide reacts with aq. NaOH by S(N)1 mechanism while n-buty...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- Why is (pm) butan-2-ol is optically inactive?
Text Solution
|
- Elimination reactions (especially beta-elimination) are as common as t...
Text Solution
|
- The treatment of ethyl bromide with aqueous KOH results ethyl alcohol ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of major monohalo compound products in each of the...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structures of major monohalo compound products in each of the...
Text Solution
|