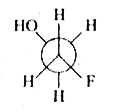
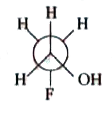
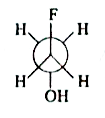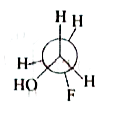A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Conformations are different arrangements of atoms that are interconver...
Text Solution
|
- In a methane (CH(4) molecule each hydrogen atom is at a corner of a re...
Text Solution
|
- Order of the bond strength of C-H bonds involving sp, sp^(2) and sp^(3...
Text Solution
|
- A) C-H bond in ethyne is shorter than C-H bonds in ethene. R) Carbon...
Text Solution
|
- The dihedral angle between two C-H bonds the staggered conformation of...
Text Solution
|
- CH4 అణువులో Hoverset^(C)H బంధ కోణం
Text Solution
|
- H-CequivC-CH=CH(2)("में")C-C एकल बन्ध के कार्बन परमाणुओं का संकरण है
Text Solution
|
- The hybridisation of carbon atoms in C-C single bond H-C equiv C-CH(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Order of the bond strength of C – H bonds involving sp, sp^(2) and sp^...
Text Solution
|