Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
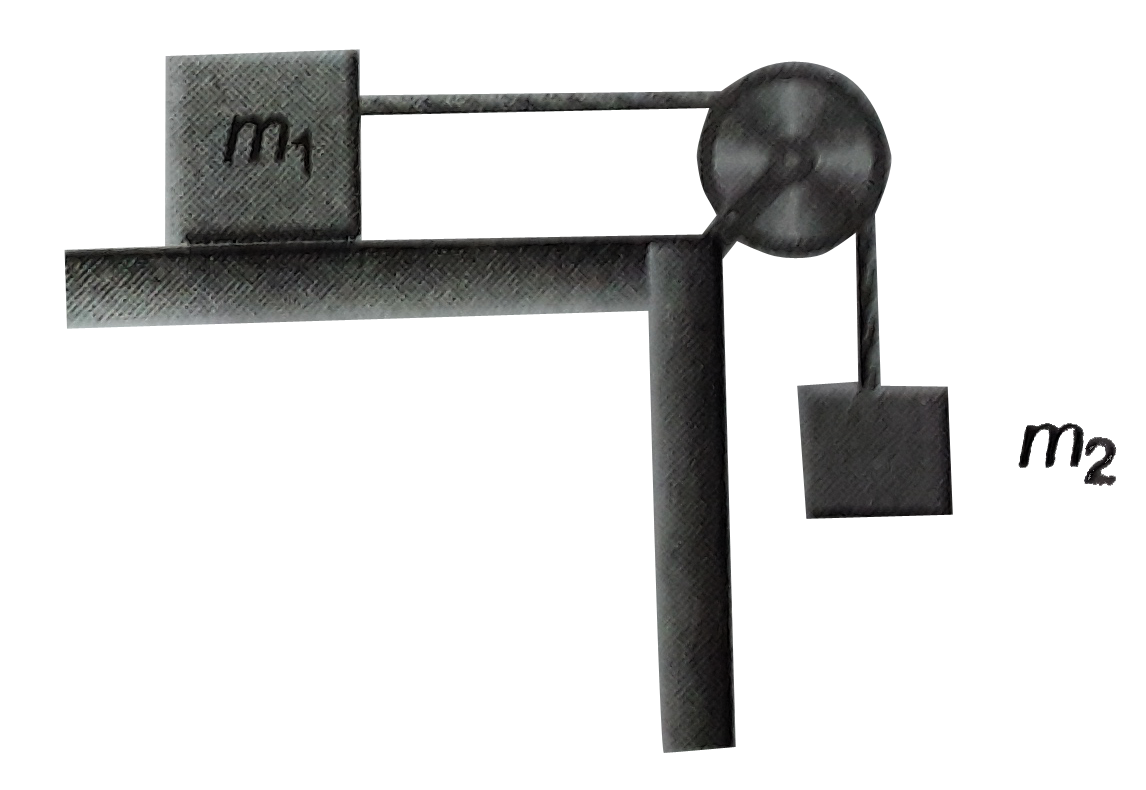
- Two masses m(1) =10 Kg and m(2)=5kg are connected by an ideal string a...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m(1) =10 Kg and m(2)=5kg are connected by an ideal string a...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected through a massless in...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m(1) and m(2) are connected as shown in the figure...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks with masses M(1) and M(2) of 10 kg and 20 kg respectively a...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure, m(1)=m(2)=10 kg . The coefficients of friction between ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown m(1)=5 kg,m(2) = 10 kg & friction coefficient betw...
Text Solution
|
- In the Fig 7.89 shown , m(2) = 2.5 kg , h = 1.5 m , the system is rele...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses M(1)=4 kg and M(2)=6kg are connected by a string ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.