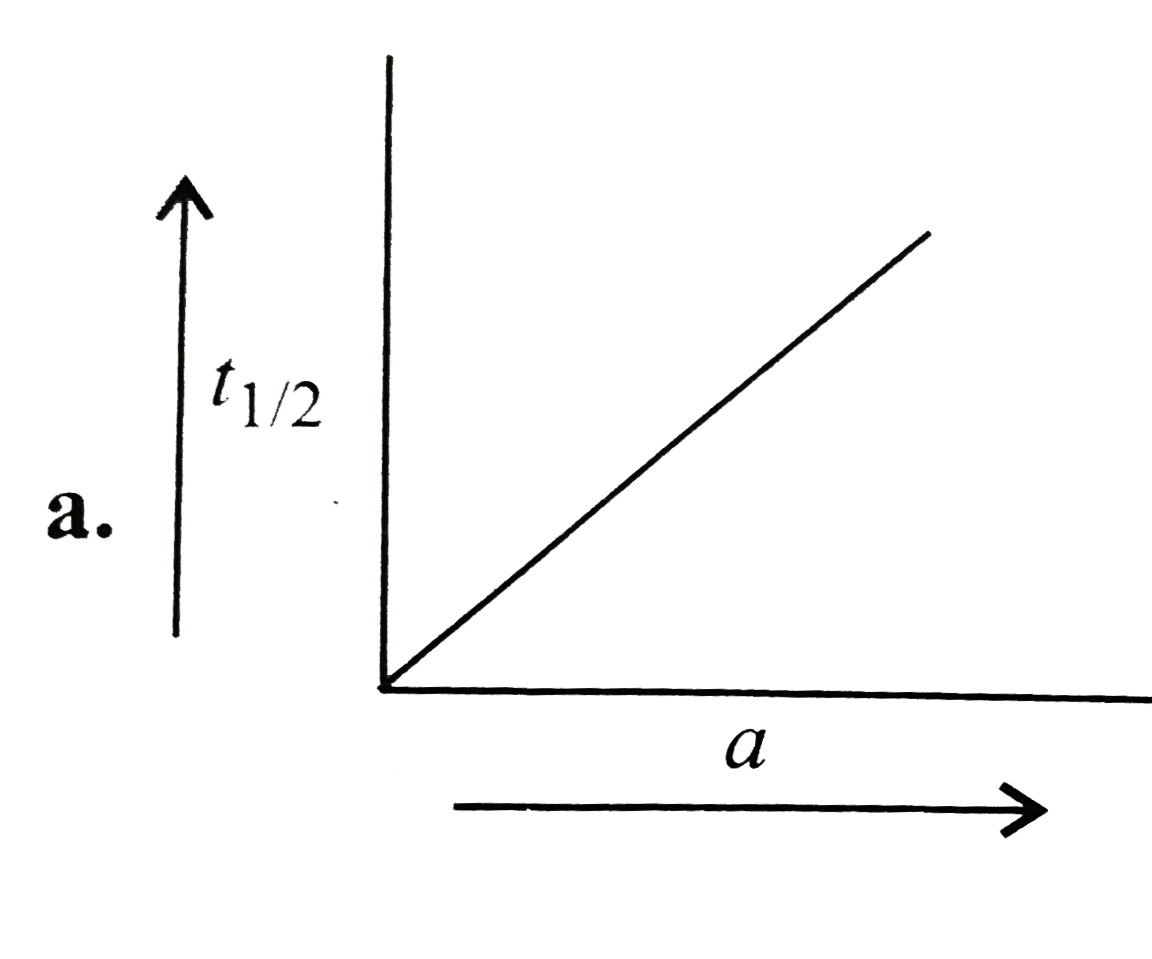
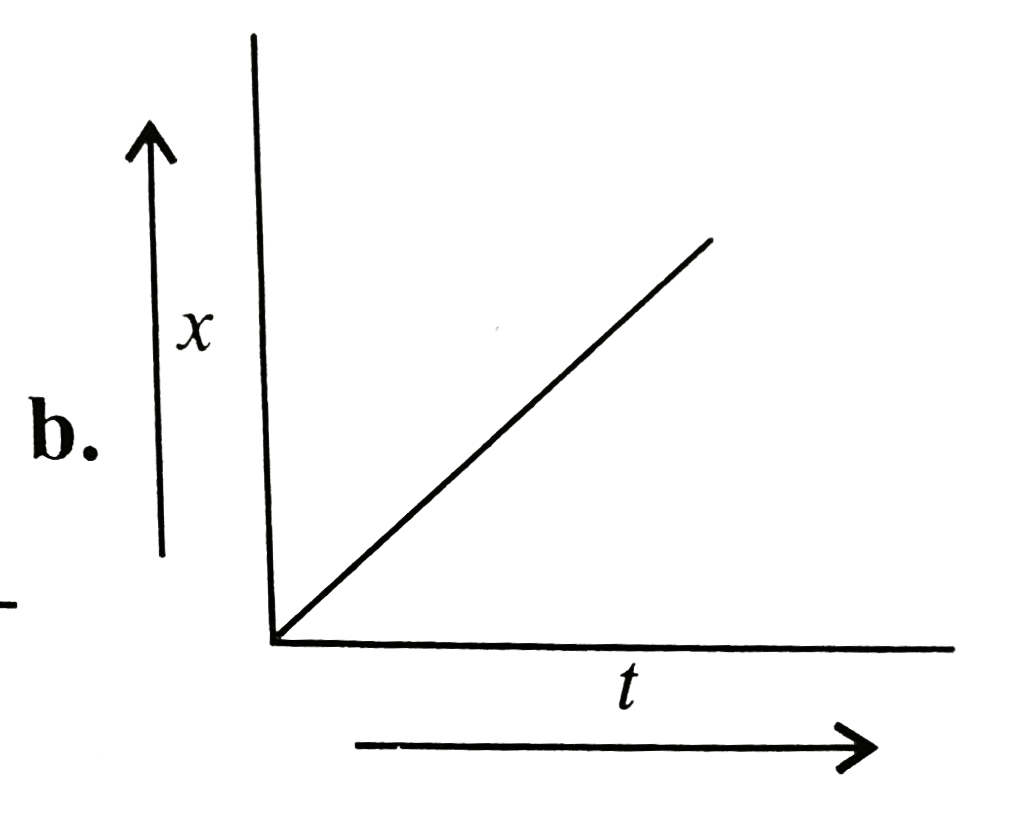
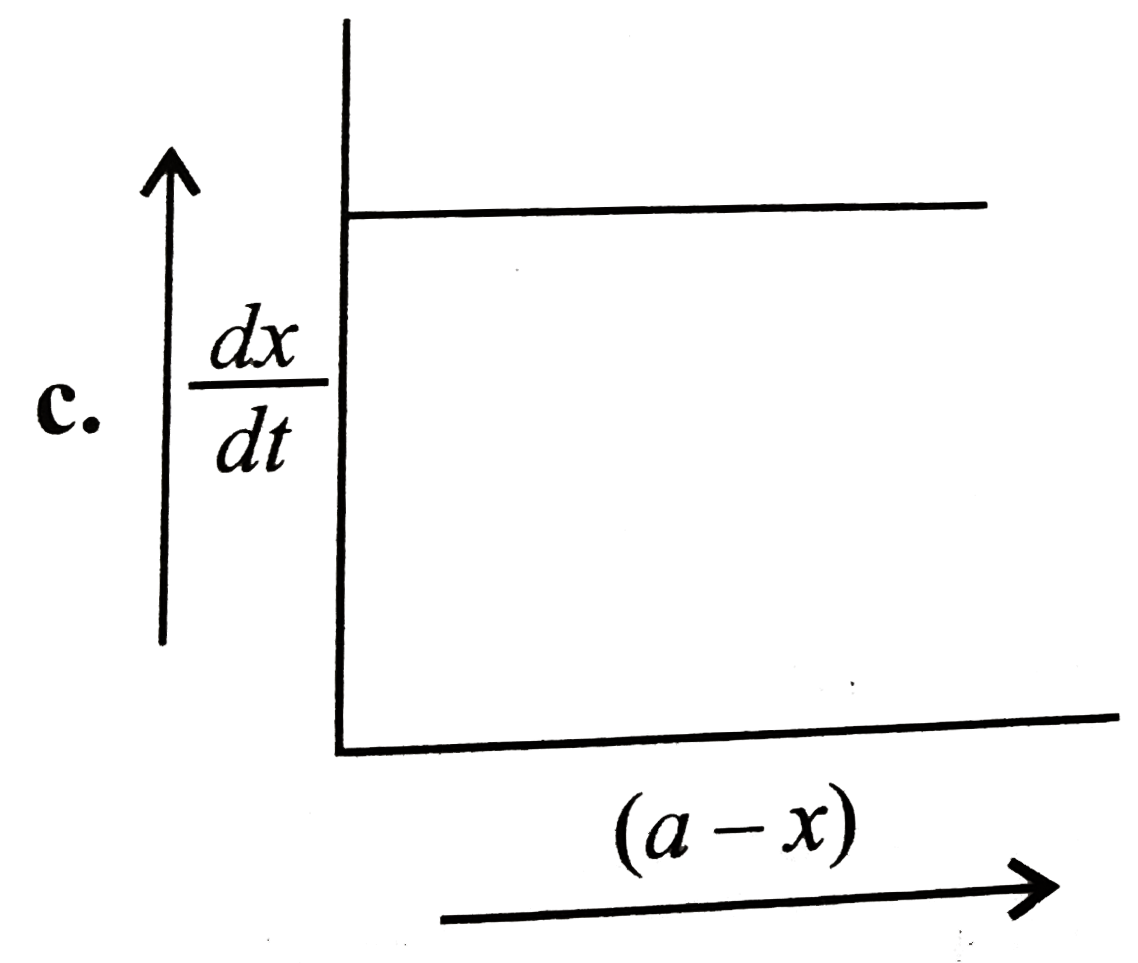
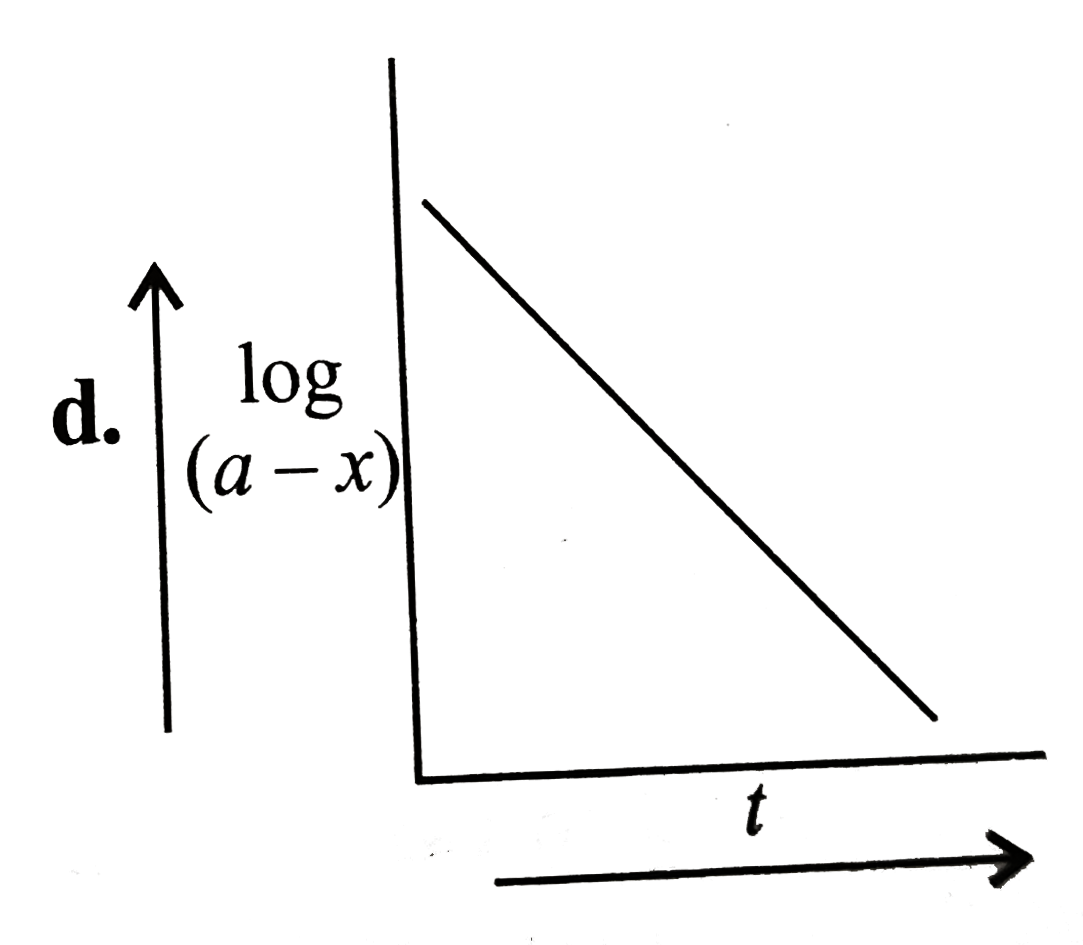
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Example|52 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 4.1 (Objective)|9 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|34 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Archives Subjective
- Which of the following graphs is not for zero order reaction?
Text Solution
|
- Rate of a reaction A + B rarr Product, is given as a function of diffe...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 20% complete in 10 min. Calculate (a) the sp...
Text Solution
|
- While studying the decompoistion of gaseous N(2)O(5), it is observed t...
Text Solution
|
- A first order gas reaction has k = 1.5 xx 10^(-6) s^(-1) at 200^(@)C. ...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction is 50% completed in 30 min at 27^(@)C and in 10...
Text Solution
|
- In a Arrhenius equation for a certain reaction, the values of A and E(...
Text Solution
|
- The decomposition of N(2)O(5) according to the equation: 2N(2)O(5)(g) ...
Text Solution
|
- Two reaction, (I)A rarr Products and (II) B rarr Products, follow firs...
Text Solution
|
- The gas phase decomposition of dimethyl ether follows first order kine...
Text Solution
|
- A first order reaction A rarr B requires activation energy of 70 kJ mo...
Text Solution
|
- form the following data for the reaction between A and B, (a) Cal...
Text Solution
|
- At 380^(@)C , the half-life periof for the first order decompoistion o...
Text Solution
|
- The ionization constant of overset(o+)(NH(4)) ion in water is 5.6 xx 1...
Text Solution
|
- The time required for 10% completion of a first order reaction at 298 ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for the first order decompoistion of a certain react...
Text Solution
|
- For the equation N(2)O(5)(g)=2NO(2)(g)+(1//2)O(2)(g), calculate the ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant of a reaction is 1.5 xx 10^(7)s^(-1) at 50^(@)C and ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate constant for an isomerization reaction, A rarr B is 4.5 xx 10...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrogenation reaction is carried out at 500 K. If the same reaction...
Text Solution
|
- The vapour pressure of two miscible liquids (A) and (B) are 300 and 50...
Text Solution
|