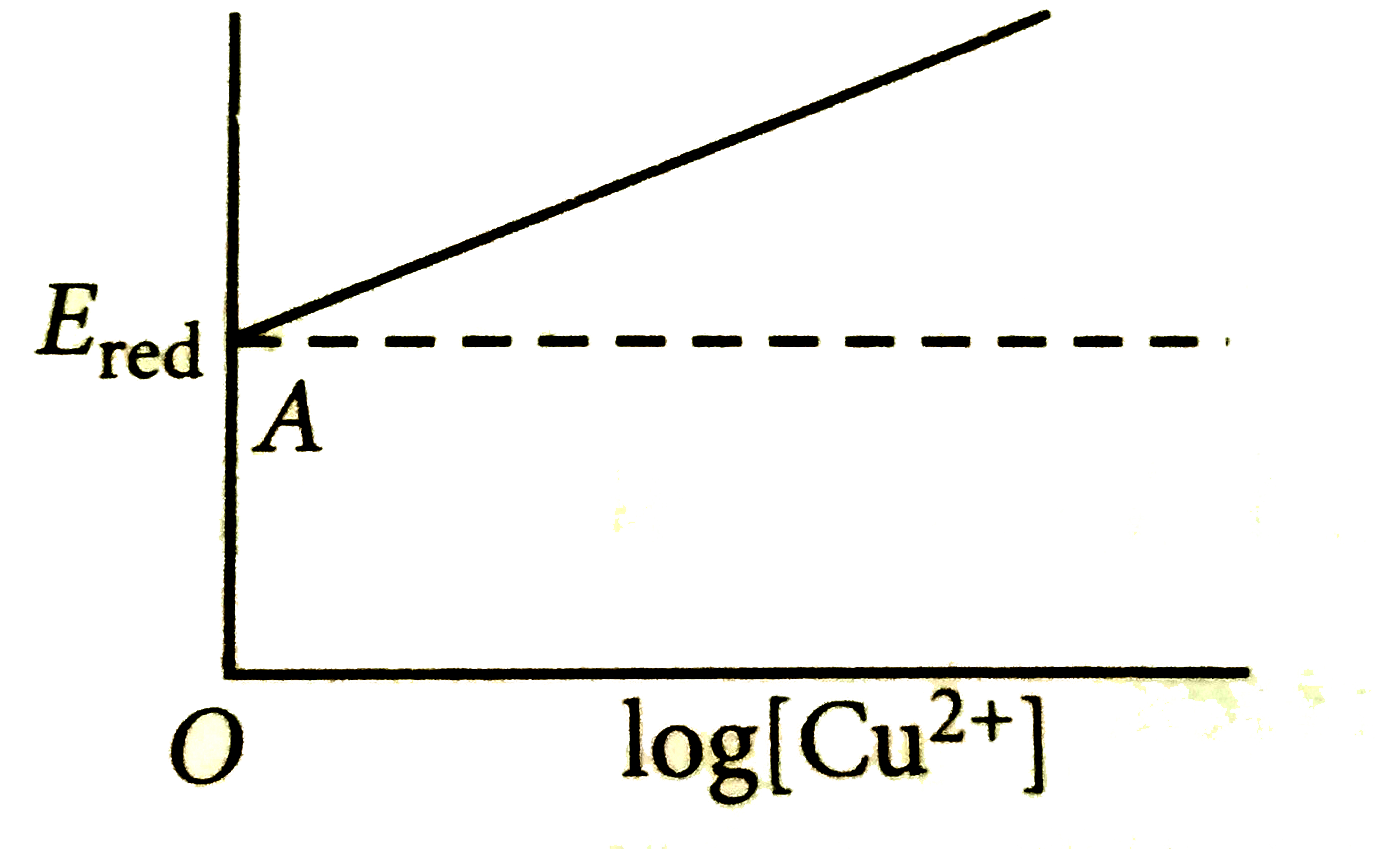A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|17 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Higher Order Thinking Skills|9 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems