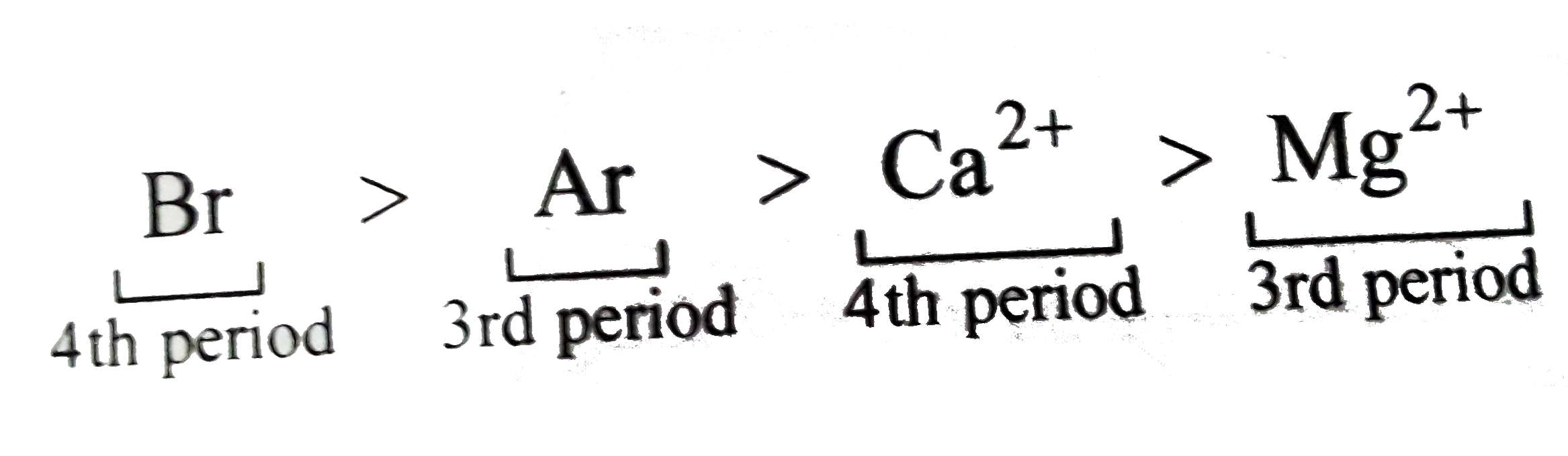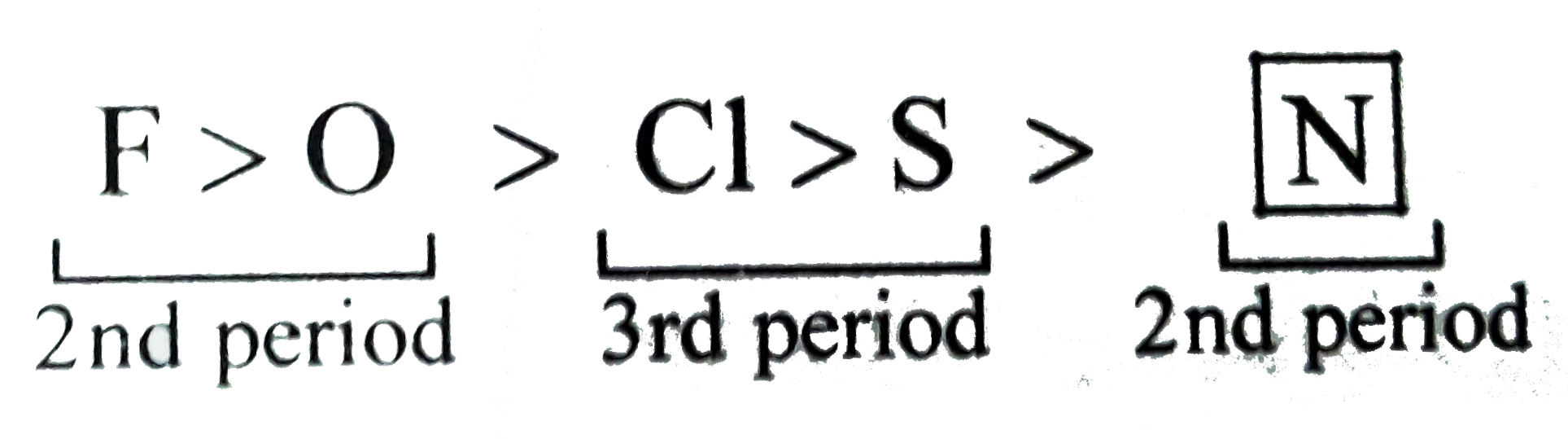Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 1.1|14 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 1.1 (Very Short)|22 VideosPERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives )Subjective|4 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 14 - CARBON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Subjective)|9 VideosPURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Assertion Reasoning Type|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-PERIODIC CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND GENERAL INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Solved Examples
- Identify the three elements A, B and C from the data given below a. ...
Text Solution
|
- Among the elements, Ar, Si, Na and Cl. Select an elements with a. Hi...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following in decreasing order as directed. (a) Decreasin...
Text Solution
|
- Predict from each set, the atom/ion which has the greatest IE(1) with ...
Text Solution
|
- The Delta(eg)H^(ɵ) of Br is 3.4 eV. How much energy in kcal is release...
Text Solution
|
- Predict from each set, the element which has the more negative electro...
Text Solution
|
- (a) The EN of cesium (Cs) is 0.7 and that of chlorine (Cl) is 3.5. Pre...
Text Solution
|
- Among the elements with Z = 9, 12 and 36, identify by atomic number of...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following question (based on ionisation energy): (a) Why...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following question (Based on EA, Delta(eg)H^(ɵ) and IE). ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following question (based on size of atoms or ions and oth...
Text Solution
|
- For the gaseous reaction K+F rarrK^(o+)+F^(ɵ) Delta H = 19 kcal mo...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction K(g)+F(g) +K^(o+)+F^(Theta) (separated ions DeltaH = ...
Text Solution
|
- From N atoms of an element A, when half the atoms transfer one electro...
Text Solution
|
- The conservation of gaseous atoms K and F to K^(o+) and F^(ɵ) absorbs ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following: a. Which of the following Na, Mg, Si and P wo...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following oxides as a. Strongly acidic b. Weakly acidic...
Text Solution
|
- Select the strongest and weakest acid in each of the following sets: ...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.10 M aqueous solution of which salt in each of the following pairs...
Text Solution
|
- Identify: a. The good oxidising agent (s) b. The good reducing age...
Text Solution
|