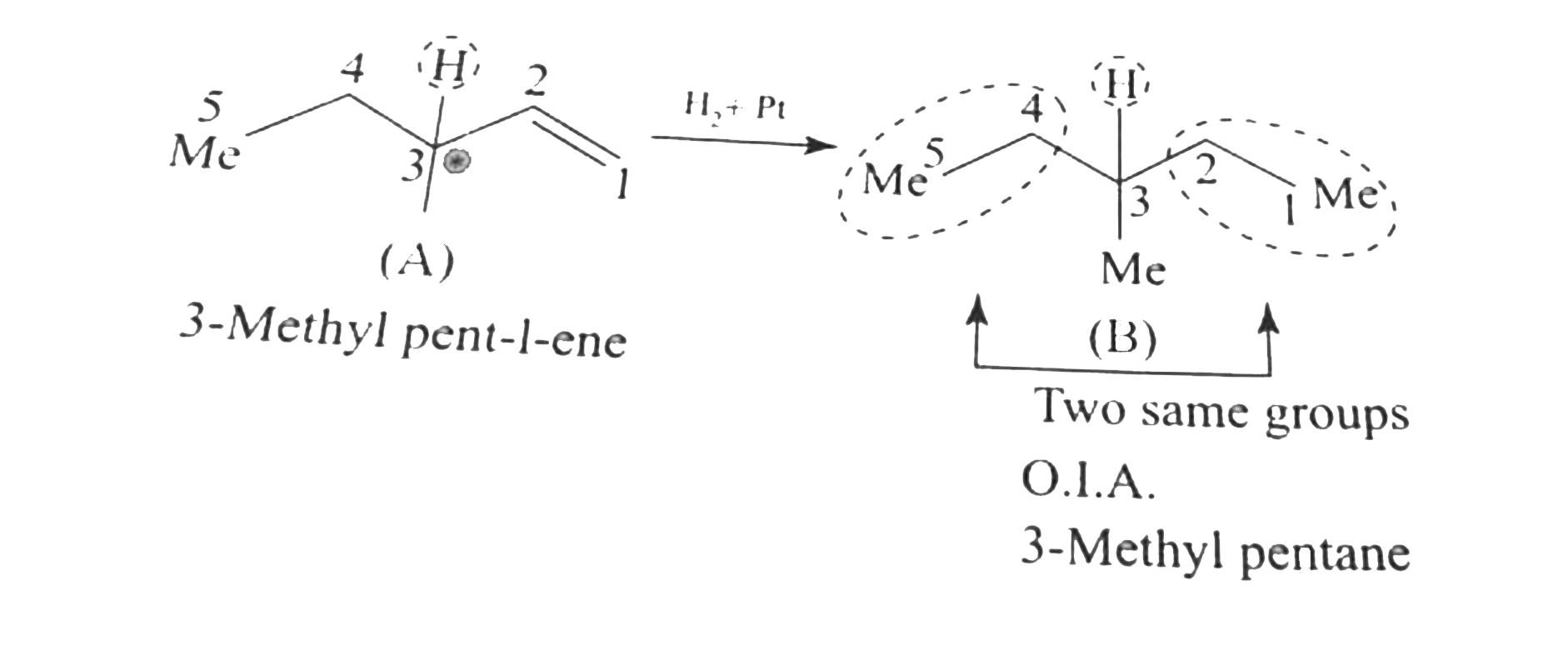
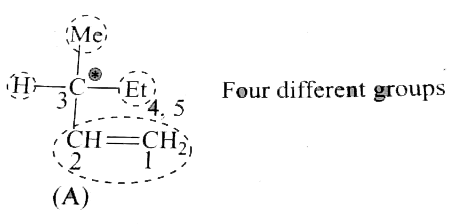Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise EXERCISES|29 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise linked Comprehension Type|38 VideosALKENES AND ALKADIENES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Single correct Answer|14 VideosALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives|13 VideosALKYNES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Archives - Analytical and Desriptive Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ALKENES AND ALKADIENES-SOLVED Example
- Give the decreasing order or reactivity for the elimination with stron...
Text Solution
|
- A compound (A) is a sodium salt of dibasic acid and on electrolysis gi...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structure of an optically active alkene (A) having the lowest...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structure of an optically active alkyne (A) having the lowest...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structure of an optically active unsaturated hydrocarbon (A) ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of (A) and (B) in the following reaction. Oct-...
Text Solution
|
- Give all the possible products from the reaction of NBS with 4-methyl ...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions : a. (F)overset (+D)larr(E)overse...
Text Solution
|
- a. b. c. Tetrachloroethane does not give the test for unsatur...
Text Solution
|
- i. Z-2,3-Dideuteroeo-but-2-ene overset("Hydrobo ration")underset("brom...
Text Solution
|
- Complete the following reactions: i. CH(2)=CH(2) overset(EtONa+eTOH)...
Text Solution
|
- a. Convert butan-1-ol to 3-chlorobutan -2-ol. b. Convert propene to:...
Text Solution
|
- Convert : a. 1-Bromobutane to 2-bromobutane b. 1-Bromobutane to 1...
Text Solution
|
- Convert:
Text Solution
|
- Write the monomer of the following polymer : a. P.M.M.A. ,b. H.D.P....
Text Solution
|
- Which of the polymer (s) in Example is // are optically active or chir...
Text Solution
|
- Based on the arrangement of branching of [(R)-(Ph), in case of styron ...
Text Solution
|
- Convert the following :
Text Solution
|
- Identify compound (A).
Text Solution
|
- Identify compound (A) and (B).
Text Solution
|