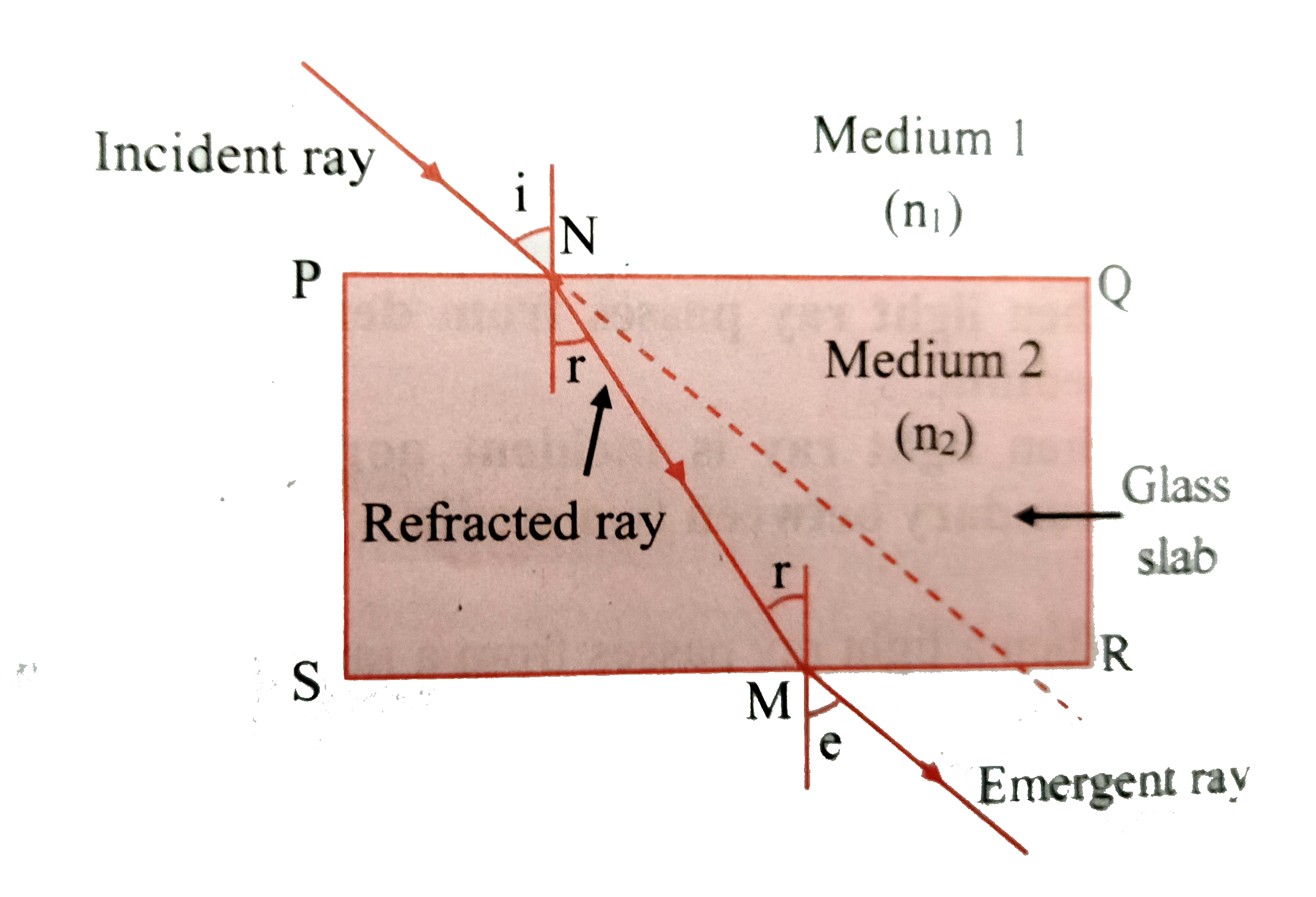
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Refraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Give reasons|2 VideosRefraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Distinguish between|1 VideosRefraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Match the following|1 VideosMODEL QUESTION PAPER PART-2
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS|2 VideosSOCIAL HEALTH
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER ASSESSMENT|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
TARGET PUBLICATION-Refraction of light-Answer the following
- If the angle of incidence and angle of emergence of a light ray fallin...
Text Solution
|
- 'During refraction of light through the glass slab, incident ray and e...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the path of refracting ray and emergence ray, if two gla...
Text Solution
|
- Use your brain power ! Will light travel through a glass slab with t...
Text Solution
|
- Use your brain power ! Will the velocity of light be same in all med...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain laws of refraction of light.
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by absolute refractive index?
Text Solution
|
- What is refraction of light? How is refractive index of material relat...
Text Solution
|
- Fill in the blanks and explain the completed sentences. i. The chang...
Text Solution
|
- Fill in the blanks and explain the completed sentences. Refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- If the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first...
Text Solution
|
- State using a neat diagram, what happens to the path of light when l...
Text Solution
|
- State using a neat diagram, what happens to the path of light when l...
Text Solution
|
- State using a neat diagram, what happens to the path of light when l...
Text Solution
|
- Give two examples of the phenomenon where refraction of light takes pl...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of Mirage .
Text Solution
|
- Explain with an example the effect of atmospheric refraction on a smal...
Text Solution
|
- Explain how twinkling of stars is an effect of atmospheric conditions ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the occurrence of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset on the b...
Text Solution
|
- Which colour deviates minimum during the dispersion of light through a...
Text Solution
|