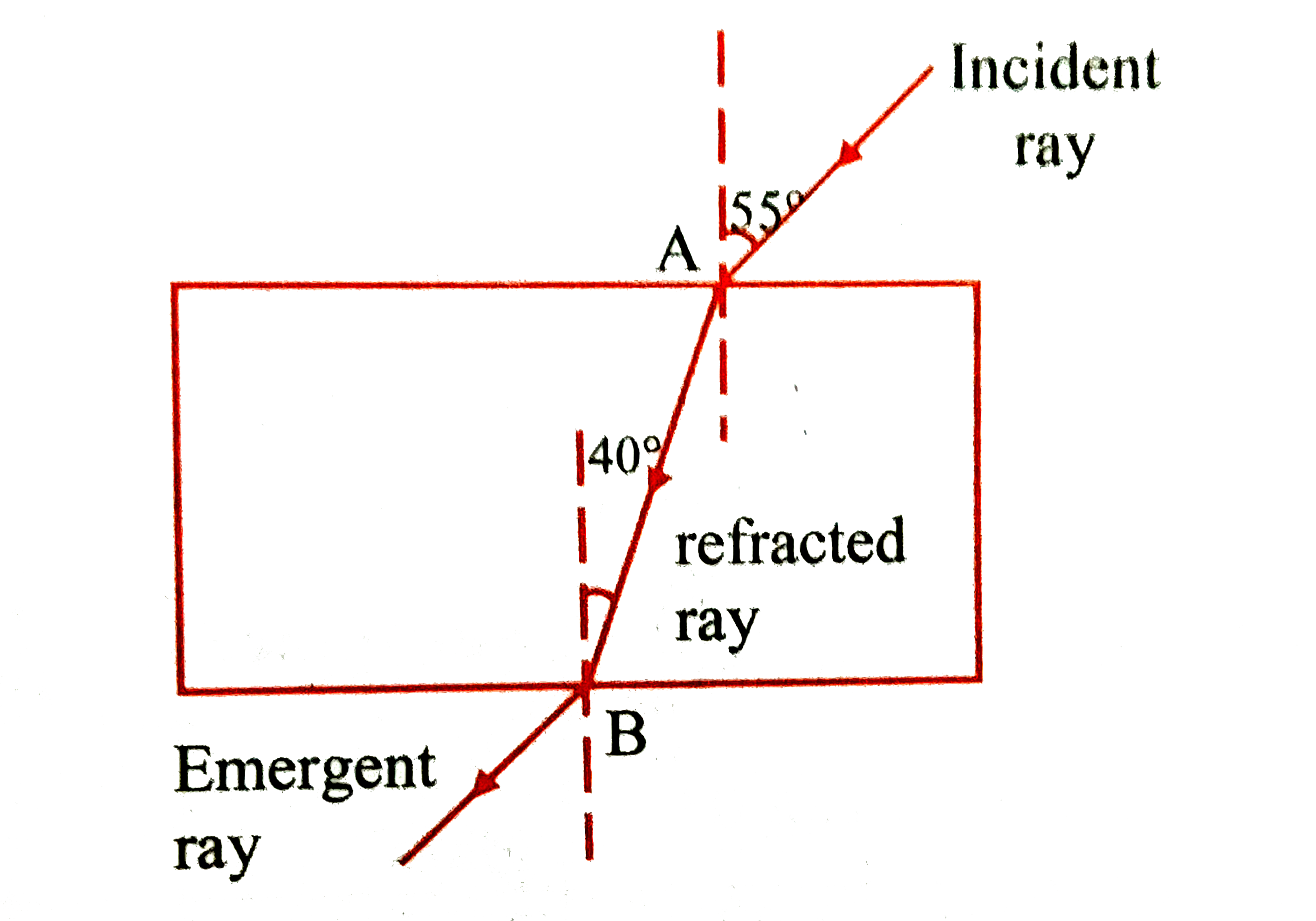
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Refraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Questions based on paragraph|8 VideosRefraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Practice problems|9 VideosRefraction of light
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise Complete the given chart/table|1 VideosMODEL QUESTION PAPER PART-2
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS|2 VideosSOCIAL HEALTH
TARGET PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER ASSESSMENT|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
TARGET PUBLICATION-Refraction of light-Questions based on diagram
- In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed tha...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed tha...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed tha...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by dispersion of white light ? Describe the formation of...
Text Solution
|
- In dispersion of sunlight by a glass prism, which colour is deviated t...
Text Solution
|
- Given figure represents formation of rainbow in the sky. Which pheno...
Text Solution
|
- Based on the below diagram, answer the following question. What d...
Text Solution
|
- Based on the below diagram, answer the following question. What d...
Text Solution
|
- Based on the below diagram, answer the following question. What d...
Text Solution
|