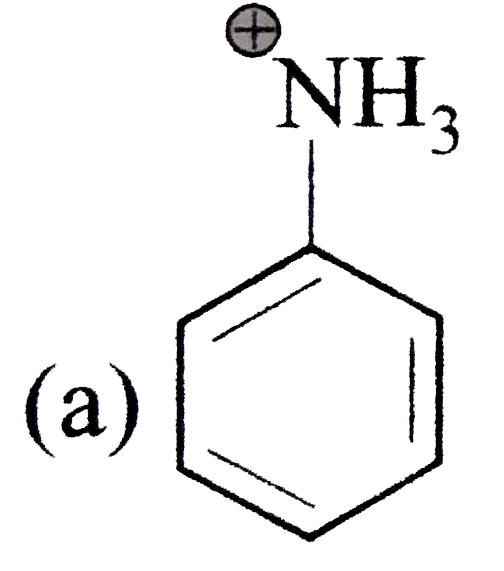
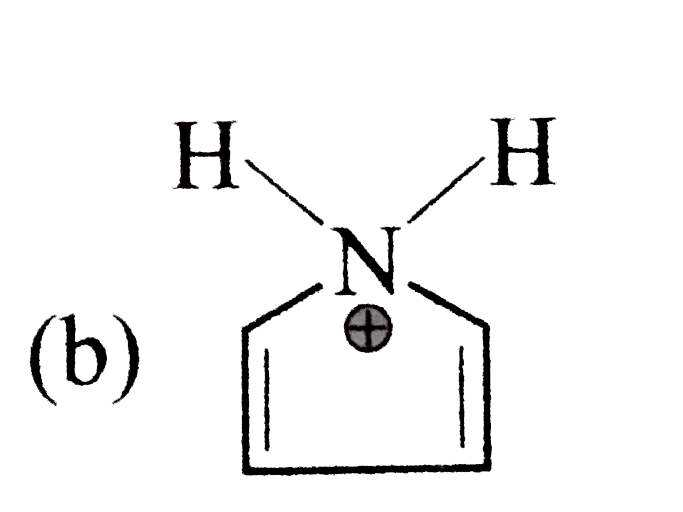
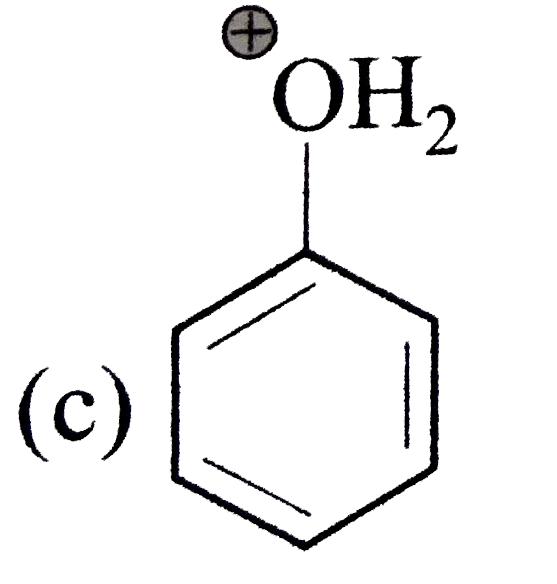
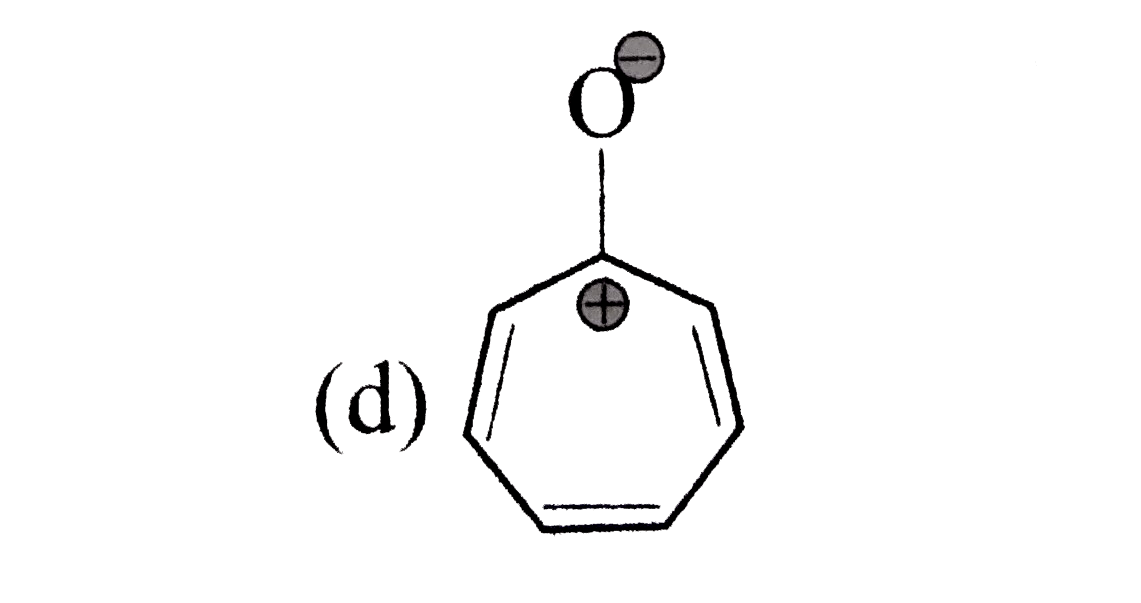
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SOME BASIC PRINCIPALS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
A2Z|Exercise Acid And Basic Strength|29 VideosSOME BASIC PRINCIPALS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
A2Z|Exercise Bond Fission, Reagents, Reactive Intermediates And Their Stability|31 VideosSOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
A2Z|Exercise Section D - Chapter End Test|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A2Z-SOME BASIC PRINCIPALS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Section D - Chapter End Test
- In which delocalisation of positive charge is possible?
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following comounds in increasing order of length of their ...
Text Solution
|
- The order of heat of hydrogenation in following compounds is:
Text Solution
|
- S(N)1 reaction is faster in
Text Solution
|
- Which compound would be least soluble in water?
Text Solution
|
- Among the following compound which can be dehydrated very easily is :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the follwing is not the characteristic of the mechanism of fr...
Text Solution
|
- Find the strongest acid among the following compound
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the dissociation constant is highest
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following compounds is most acidic
Text Solution
|
- The optically active tartaric acid is named as D-(+)- tartaric acid be...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following compounds (I-II) the correct order of reaction wit...
Text Solution
|
- The following reaction is described as
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the most stable cation?
Text Solution
|
- The observed dipole moment of nitromethane is highly than the dipole m...
Text Solution
|
- Dehydrohalogenation in presence of OH^(-) is correct represented by
Text Solution
|
- Among the following the aromatic compound is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds are not arranged in order of decreasi...
Text Solution
|
- Most stable carbonium ion is :
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following species is most stable
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following gives most stable carbocation by dehydration
Text Solution
|