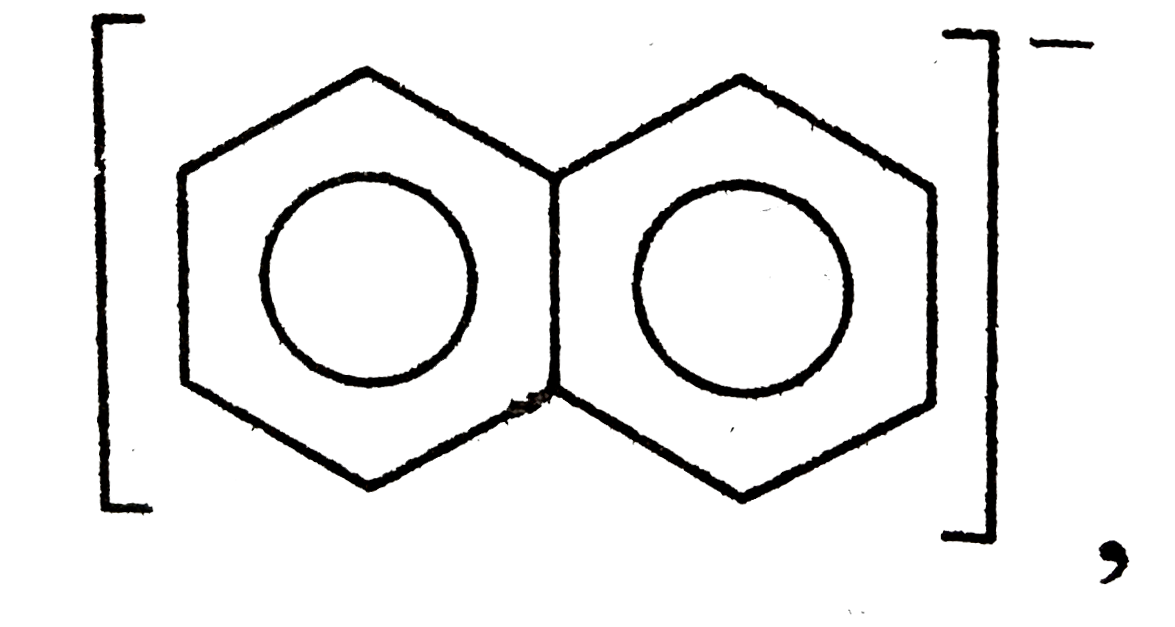
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
R SHARMA-POLYMERS-All Questions
- Which of the following statement is correct about Ziegler-Natta Cataly...
Text Solution
|
- Among the polymers, which one is generally prepared by cationic polyme...
Text Solution
|
- Anionic polymerization may be accomplished with
Text Solution
|
- The polymerization process in which two or more chemically different ...
Text Solution
|
- Copolymerization of vinyl chloride and vinylidene chloride in a 1 : 4 ...
Text Solution
|
- Lexan is a polymer of usually high impact strength and is used to make...
Text Solution
|
- Bubble gum contains
Text Solution
|
- Melmac, a thermosetting plastic often used to make plastic dishes, is ...
Text Solution
|
- The copolymer of vinyl chloride and crylonitrile, which is used for s...
Text Solution
|
- Rubber is vulcanized to form
Text Solution
|
- Buna -S rubber (SBR) is a copolymer of
Text Solution
|
- Gutta-percha, a naturally occurring highly crystalline non elastic rub...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement about polymers in correct?
Text Solution
|
- The poly dispersity index (PDI) is for - natural polymers
Text Solution
|
- PHBV is a copolymer of
Text Solution
|
- Nylon - 2 nylon - 6 is a copolymer of glycine and
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following sequence of reation HC -= CH underset(2 HCL)o...
Text Solution
|
- Nylon 6, 6 is an example of
Text Solution
|
- Natural rubber is a polymer of
Text Solution
|
- In elastomers, the intermolecular forces are
Text Solution
|