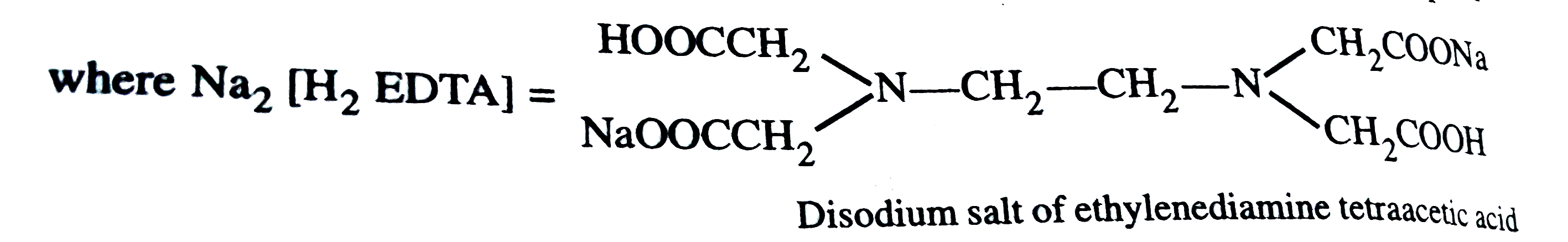
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (Matching Type Questions)|3 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (Assertion and Reason type question )|3 VideosCLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
PRADEEP|Exercise NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (Multiple Choice Questions -II)|10 VideosCHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
PRADEEP|Exercise Curiosity Questions|2 VideosENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
PRADEEP|Exercise COMPETITION FOCUS (JEE(Main and Advanced)/Medical Entrance (VI.ASSERTION-REASON) Type II|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES -NCERT (EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS) (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS)
- Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine. Why?
Text Solution
|
- All transition element are d- block element but all d- block elem...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the group nad valency of the elements having atomic number 11...
Text Solution
|
- Ionisation enthalpies of element of second period are given belo...
Text Solution
|
- Among the elements B, AI,C and Si, (i) Which elements has the highes...
Text Solution
|
- Write four characteristic properties of p- block elements
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct order of atomic radii of fluorine and neon (in...
Text Solution
|
- Illustrate by taking examples of transition elements and non-transitio...
Text Solution
|
- Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negati...
Text Solution
|
- First member of each group of representative elements (i.e., s and p-b...
Text Solution
|
- p-Block element form acidic basic and amphoteric oxides . Expla...
Text Solution
|
- How would you explain the fact that the first ionisation enthalpy of s...
Text Solution
|
- What do you undestand by exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction?...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the elements N, P, O and S in the order of i) increasing fir...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following a) Electronegatively of elements increase on m...
Text Solution
|
- How does the metallic and non-metalic character vary on moving from le...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of Na^(+) cation is less than that of Na atom. Give reason.
Text Solution
|
- Among alkali metals which element do you expect to be least electroneg...
Text Solution
|