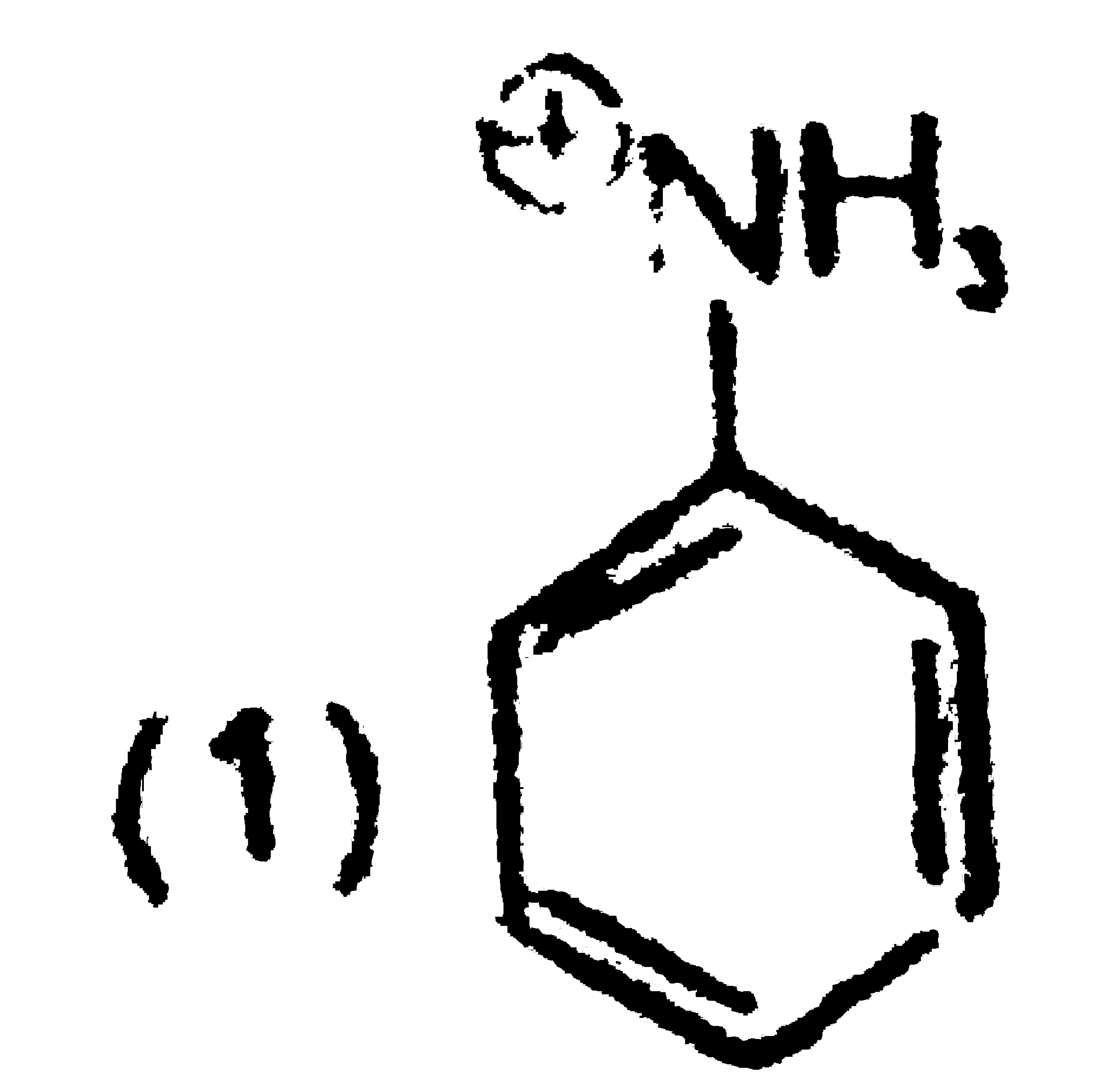
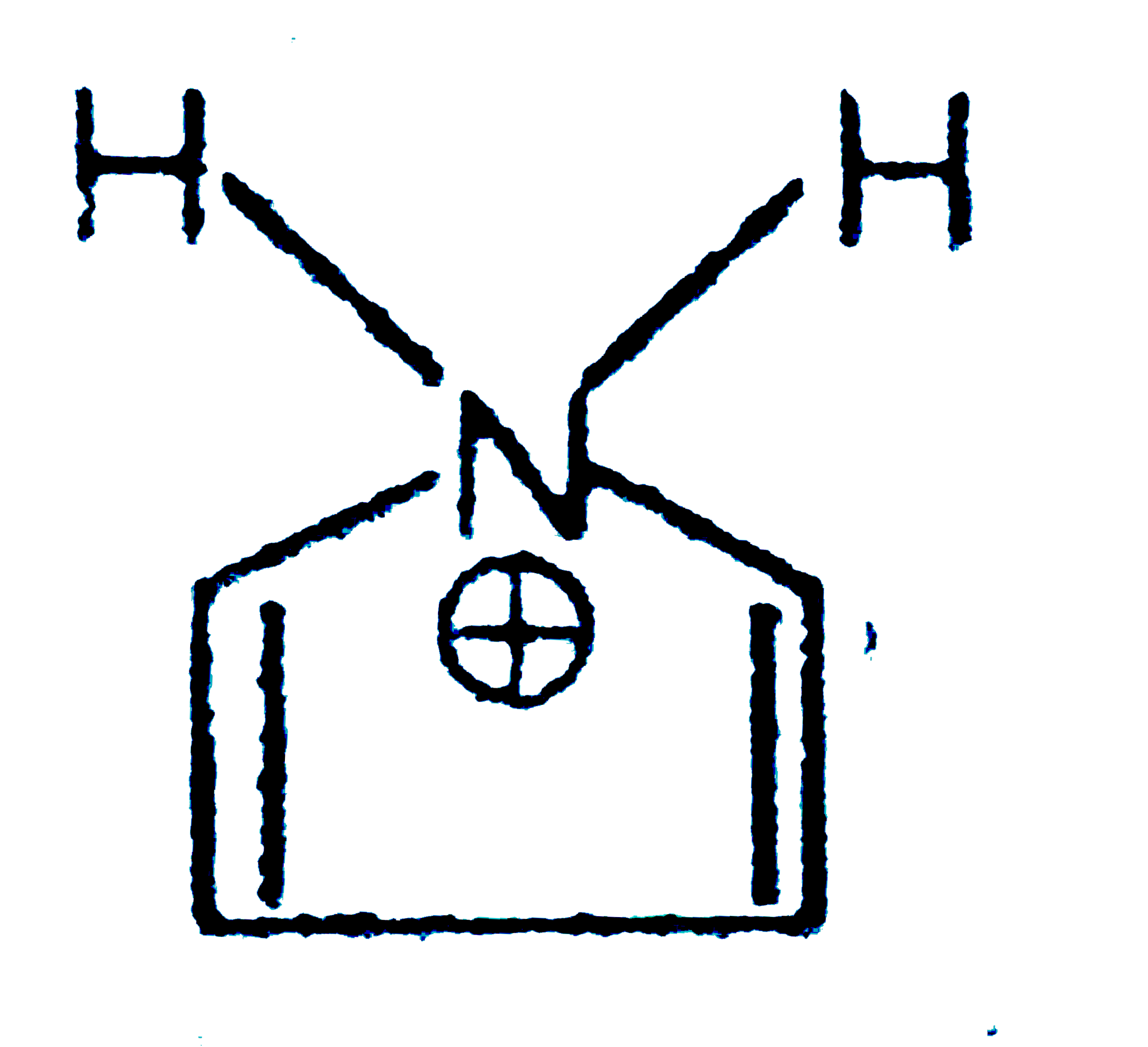
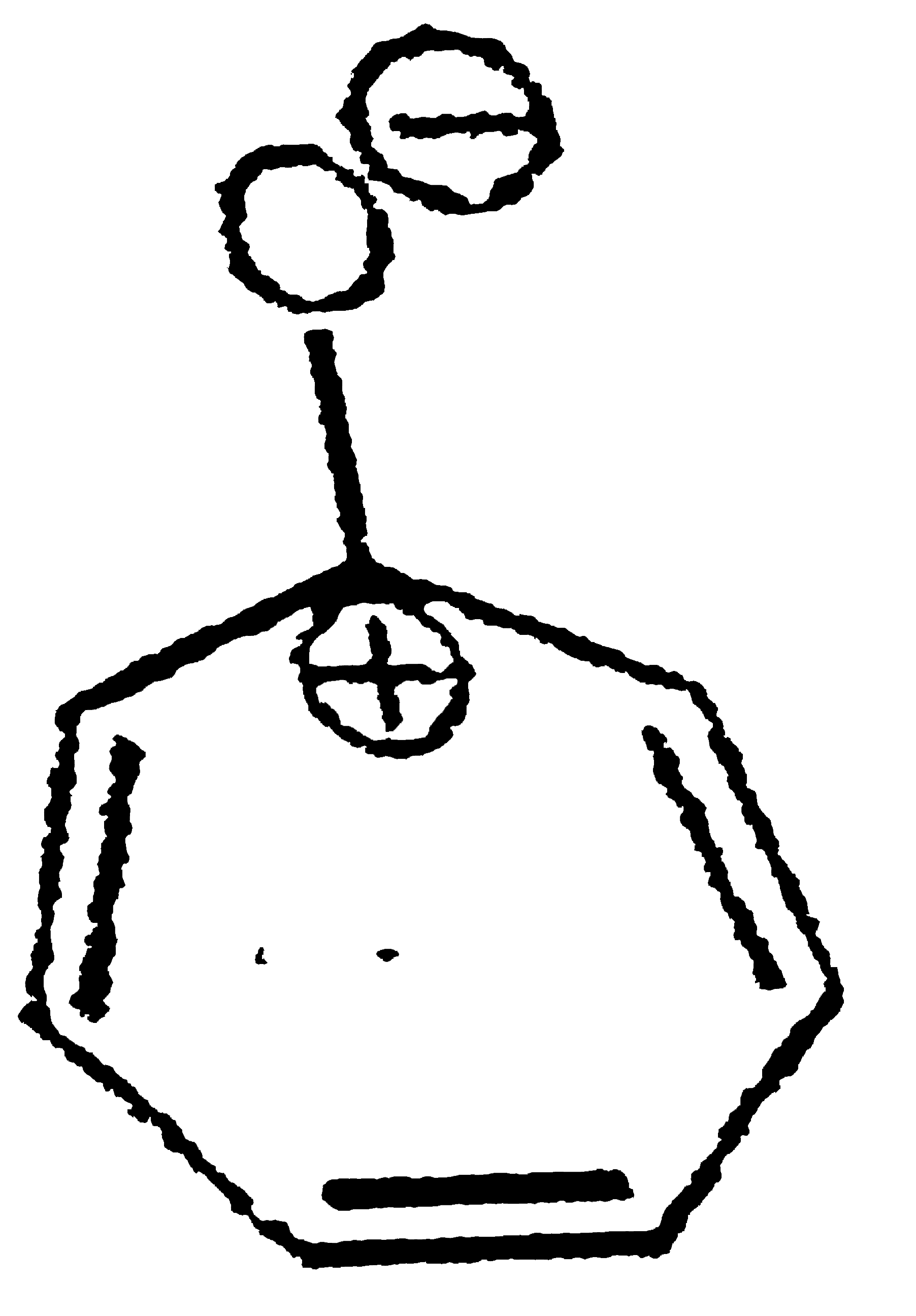
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPT-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Fundamental Concept )
- The chemical system that is non- aromatic is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the least stable carbanion?
Text Solution
|
- Arrange stability of the given carbocation in decreasing order :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compound give solvolysis reaction with slowest ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following alkoxides is the most reactive nucleophile?
Text Solution
|
- Which is the correct matched for the following reactions
Text Solution
|
- Which is correctly matched
Text Solution
|
- The correct increasing order of the reactivity of halides for S(N) 1 r...
Text Solution
|
- Reaction intermediate of EicB reaction is :
Text Solution
|
- Select false statement from the following ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not electrophile ?
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is incorrect :
Text Solution
|
- The correct leaving group ability order is :
Text Solution
|
- CH(3)-CH(2)-O-CH(2)-Clunderset("other")overset(CH(3)MgBr)rarr Which ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not a nucleophile ?
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct option : S(1) : Catechol is less acidic than reso...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction is : CH(3)CHBr-CH(2)Br+2KOH("alc.")overset(Delta)rarr C...
Text Solution
|
- For the following (i) I^(-) (ii) Cl^(-) (iii) Br^(-) the increasin...
Text Solution
|
- Orbital interation ( partial overlapping ) between the sigma bonds of ...
Text Solution
|
- In which delocalisation of positive charge is possible
Text Solution
|