Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRY
SURA PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit Test (Section -C)|2 VideosGEOMETRY
SURA PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit Test (Section -D)|2 VideosGEOMETRY
SURA PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit Test (Section -A)|5 VideosCREATIVE QUESTION SET
SURA PUBLICATION|Exercise Multiple Choice Question|120 VideosGOVT. MODEL QUESTION PAPER-2019-20
SURA PUBLICATION|Exercise Part-IV|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SURA PUBLICATION-GEOMETRY-Unit Test (Section -B)
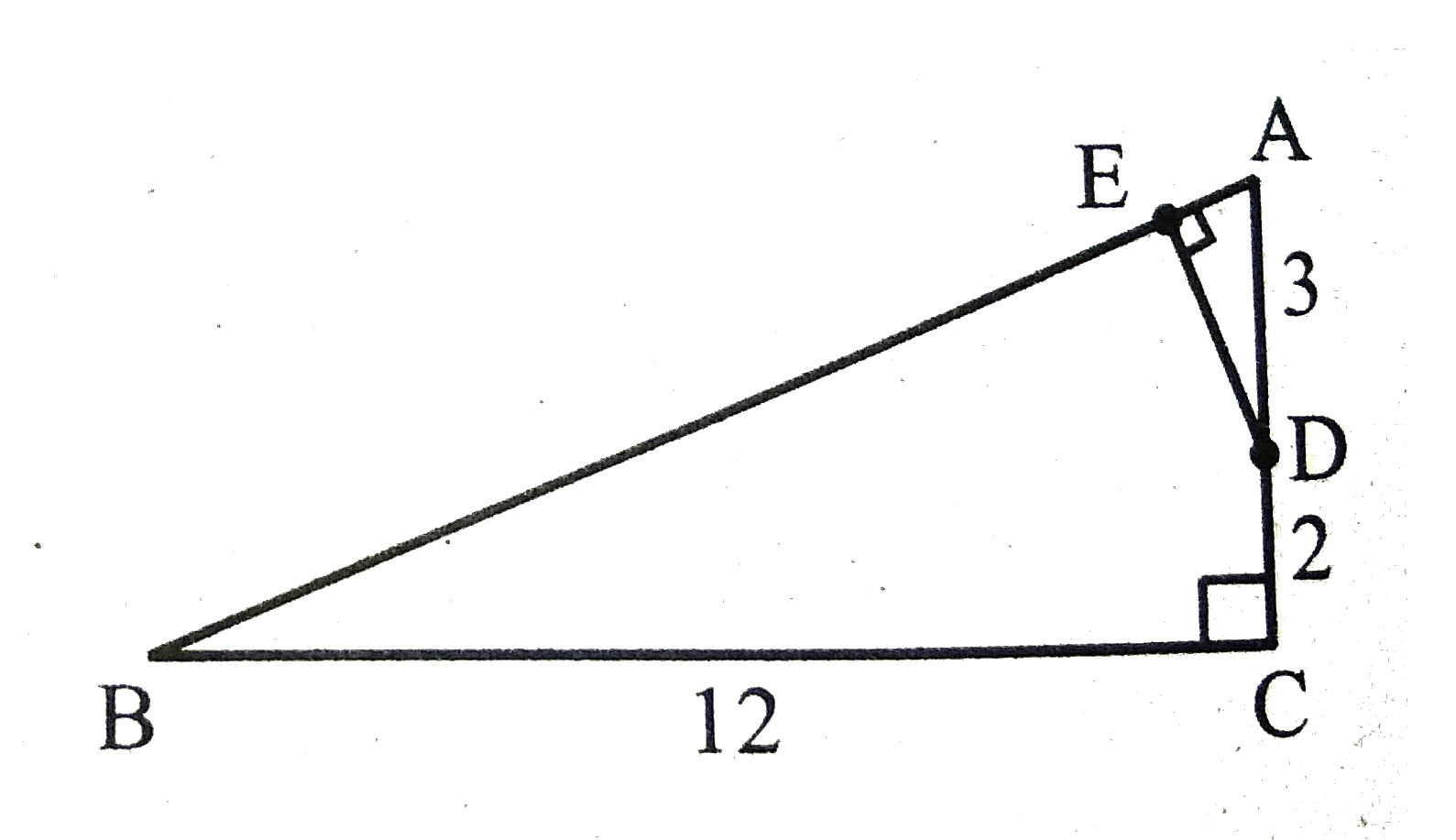
- In the adjacent figure, Delta ABC is right angled at C and DE bot AB. ...
Text Solution
|
- In figure DE|| BC and CD||EF. Prove that AD^(2)=AB xx AF.
Text Solution
|
- A man goes 18 m due east and then 24 m due north. Find the distance of...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a tangent at any point R on the circle of radius 3.4 cm and centr...
Text Solution
|
- In two concentric circles, a chord of length 16 cm of larger circle be...
Text Solution
|
- The length of the tangent to a circle from a point P, which is 25 cm a...
Text Solution
|
- To get from point A to point B you must avoid walking through a pond. ...
Text Solution
|