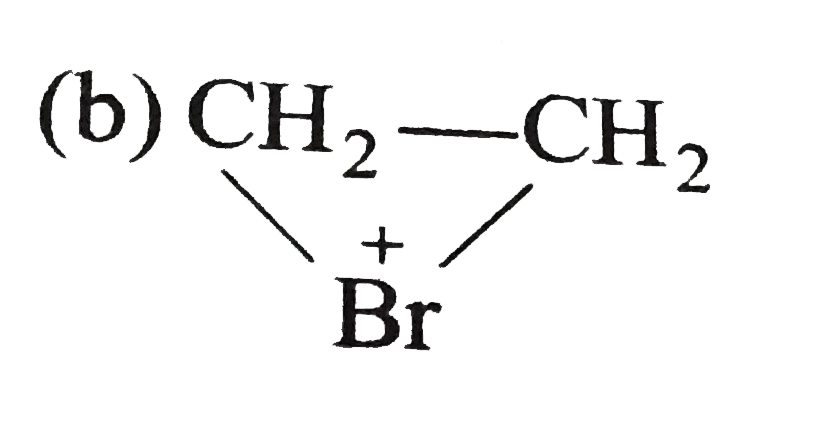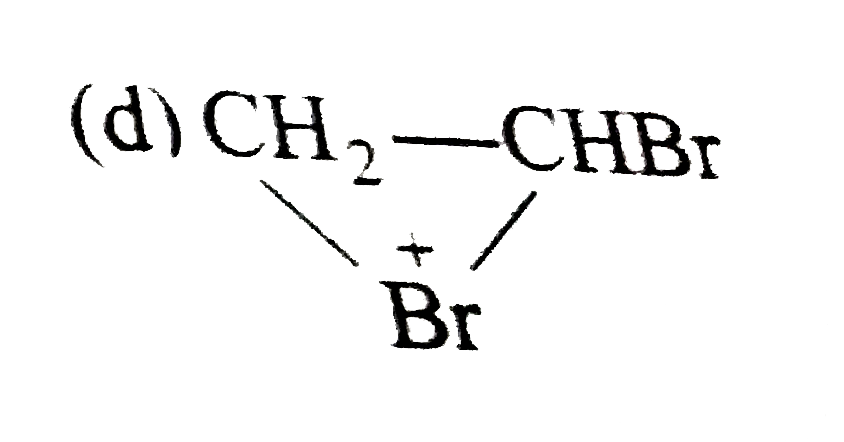A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HIMANSHU PANDEY-HYDROCARBONS (ALKANE, ALKENE and ALKYNE)-Level 1 (Q.26 To Q.50)
- Which of the following reaction will lead to creation of two chiral ce...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction of ethylene with Br(2) in water in the presence of NaCI g...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrocarbon C(8)H(14) consumes only one mole of H(2) on catalytic hy...
Text Solution
|
- Dipole moment of which compound will be maximum ?
Text Solution
|
- Correct order of reactivity towards electrophilic additon reactions is...
Text Solution
|
- Rank the following in order of statbility (lower to highest) (I)
Text Solution
|
- The following two compounds are:
Text Solution
|
- Compound (A) on oxidation withg OsO(4)//NaIO(4) gives hexanedial.Struc...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are:
Text Solution
|
- Index of unsaturation (H-deficiency)ofC(8)H(10) is…and if it has a six...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following yields But-2 ene on dehydration with conc.H(2)S...
Text Solution
|
- An alcohol (a) on dehydration gives (B), which on ozonolysis gives ace...
Text Solution
|
- which of the following compound undergoes dehydrochlorination most eas...
Text Solution
|
- Which is most easily dehydrohalogenated ?
Text Solution
|
- Cyclohexene on reaction with OsO(4) followed by reaction with NaHSO(3)...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following incorrect sttement (s) is//are:
Text Solution
|
- Ethylene reacts with Br(2) to give 1,2-dibromoethane.The anti addition...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions will result in the formation of a chi...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a hydrocarbon on ozonolysis yields one mole of glyoxal and...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrocarbon (A) on chlorinatio gives (B) ,which on reacting with alc...
Text Solution
|