A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-2 (OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS (NEET))|17 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE - 3 SECTION -A (Previous Year Problems (NEET ))|38 VideosPHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT
MOTION|Exercise QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE|12 VideosOPTICS
MOTION|Exercise Exercise|45 VideosPROJECTILE MOTION
MOTION|Exercise EXERCISE-3 (SECTION-B)|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MOTION-PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT -EXERCISE-1 (OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS)
- Light of wavelength 3320 Å incidents on metal surface (work fun...
Text Solution
|
- Using light of wavelength 6000 Å stopping potential is obtained ...
Text Solution
|
- When light source is placed at 1 m distant from photo electric...
Text Solution
|
- In the given diagram if V represent the stopping potential and...
Text Solution
|
- Photoelectric current as a function of voltage V for different ...
Text Solution
|
- In the following figure the curves have been drawn between the...
Text Solution
|
- When monochromatic light of wavelength lambda illuminates a metal surf...
Text Solution
|
- If the wavelength of incident light decrease from lamda 1 ...
Text Solution
|
- The retarding potential for having zero photo - electron current
Text Solution
|
- In photoelectric effect work function of any metal is 2.5 eV. ...
Text Solution
|
- When ultraviolet light of wavelength 100 nm is incident upon silver pl...
Text Solution
|
- Slope of V(0) vs v curve is (where V(0)= Stopping potential, v=subject...
Text Solution
|
- Figure represents the graph of photo current I versus applied ...
Text Solution
|
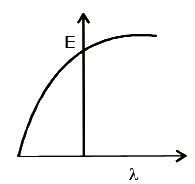
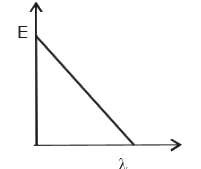
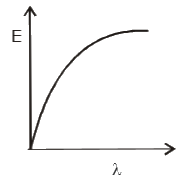
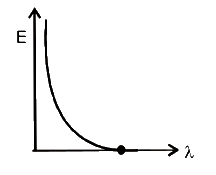
- The graph between the energy of photoelectrons E and the wav...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram, graph are drawn between stopping potential ...
Text Solution
|
- For a photoelectric cell, the graph shown the variation of c...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic source of light operation at 200 W emits 4xx10^(20) ph...
Text Solution
|
- Light of wavelength 5000 Å falls on a sensitive surface. If th...
Text Solution
|
- In photoelectric equation hv = hv 0 + (1 )/(2) mv ^ 2 of Ei...
Text Solution
|
- the photoelectric effect can not be explained by the wave theory of li...
Text Solution
|