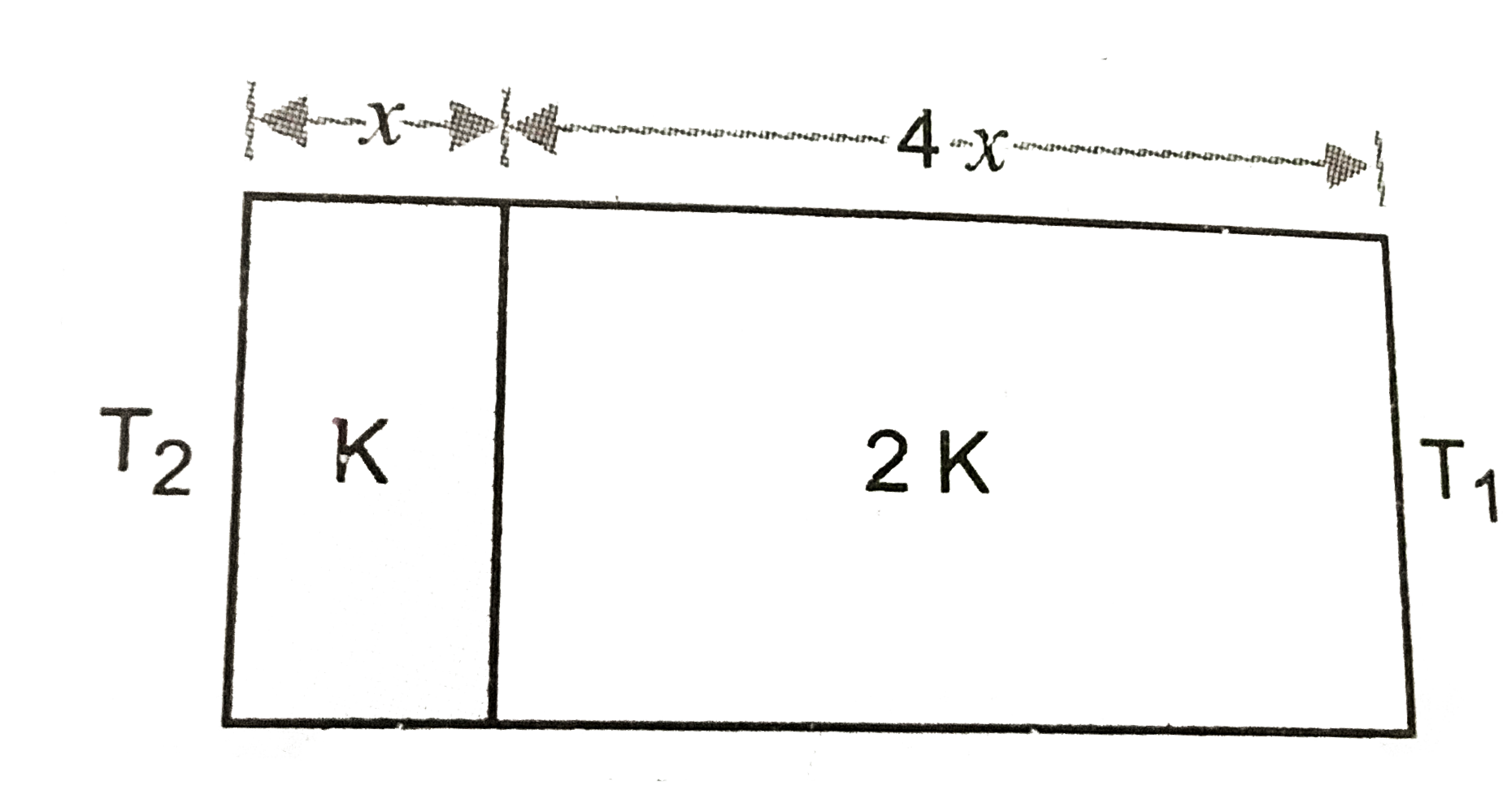
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise NCERT Exemplar|8 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|10 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Newton'S Law Of Cooling|3 VideosSYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTIONS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
NCERT FINGERTIPS|Exercise Assertion And Reason|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT FINGERTIPS-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-Higher Order Thinking Skills
- The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab, consist...
Text Solution
|
- A wall of dimensions 2.00 m by 3.50 m has a single-pane window o...
Text Solution
|
- The figure show a cross-section of a double glass unit of a window ...
Text Solution
|
- In question number 3, the thermal conductivity (in W m^(-1) K^(-1)...
Text Solution
|
- A lake surface is exposed to an atmosphere where the temperature is lt...
Text Solution
|
- Two chunks of metal with heat capacities C(1) and C(2), are interconne...
Text Solution
|
- A double pan window used for insulating a room thermally from outside ...
Text Solution
|
- In question number 7, the temperature of other interfaces (in .^(...
Text Solution
|