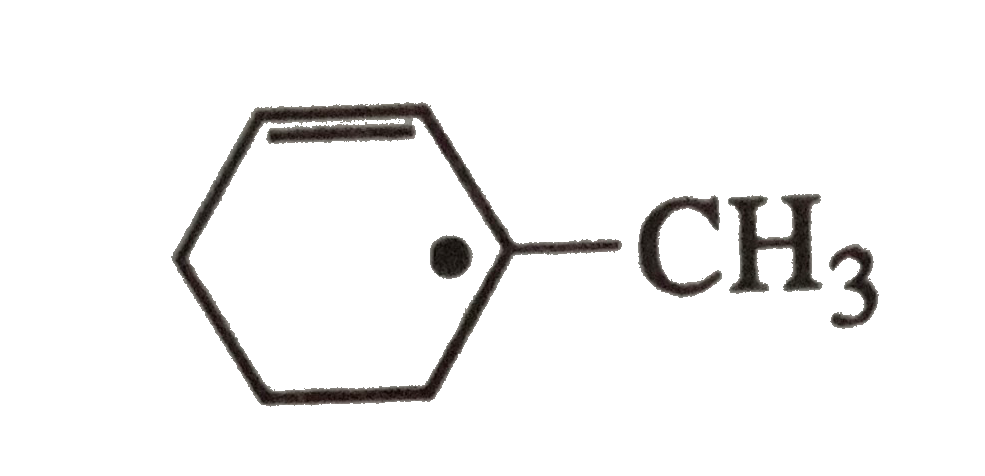
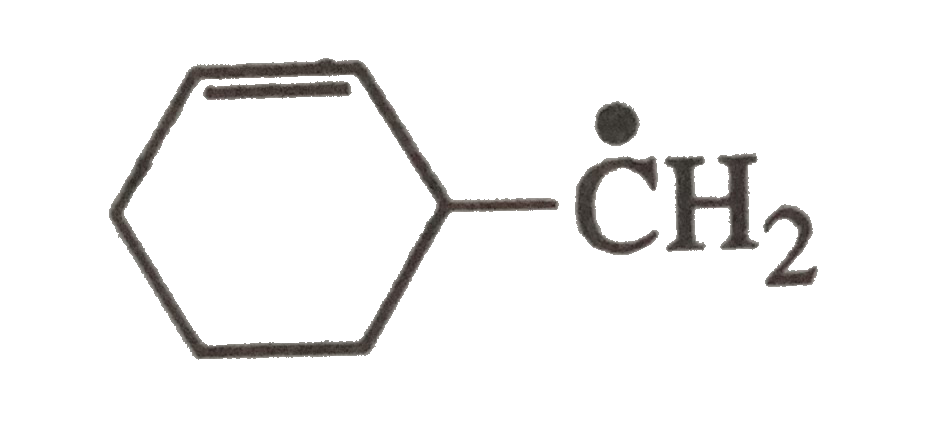
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise SELECTED STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE MCQS|64 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise LINKED COMPREHENSION TYPE MCQS|10 VideosBASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Matrix Type Questions|2 VideosALKALI EARTH METALS
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit test-12|5 VideosBIOMOLECULES
DINESH PUBLICATION|Exercise MATRIX - MATCH TYPE|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DINESH PUBLICATION-BASIC PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-REVISION QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITIVE EXAMS.
- Which of the given statement(s) about N, O, P and Q with respect to M ...
Text Solution
|
- In the replacement reaction rarrC-I+MF rarr rarr C-F+MI The react...
Text Solution
|
- The radical is aromatic because it has
Text Solution
|
- The structure of isobutyl group in an organic compound is
Text Solution
|
- Structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-2-hydroxy-4-meth...
Text Solution
|
- The order of stability of the following carbocations underset((I))(...
Text Solution
|
- The hyperconjugative stabilities of tert-butyl cation and 2-butene, re...
Text Solution
|
- Among P, Q, R and S, the aromatic compounds(s) is/are
Text Solution
|
- Most stable radical is
Text Solution
|
- The IUPAC name of the following compound is :
Text Solution
|
- The which is not used as gaseous fuel :
Text Solution
|
- The petrol of octane number 80 has :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not a an allylic halide ?
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following is not correct in respect to hybridization ...
Text Solution
|
- The correct IUPAC name of the following compound is : H(3)C-CH=under...
Text Solution
|
- IUPAC name of overset(5)CH(3)-overset(4)underset(OH)underset(|)CH-over...
Text Solution
|
- Mesomeric effect involves
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is an aromatic species ?
Text Solution
|
- The relative stability of the following carbocations in decreasing ord...
Text Solution
|
- The IUPAC name of the compound X is
Text Solution
|