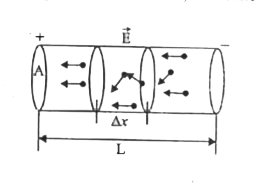
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICAL PROBLEMS AND ANSWERS|29 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise THREE MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS|11 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise THREE MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS|4 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
SUBHASH PUBLICATION|Exercise NUMERICALS WITH SOLUTIONS|21 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-FIVE MARK QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
- Derive an expression for electrical conductivity.
Text Solution
|
- State the laws of resistance of a conductor. Define specific resistanc...
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on the variation of resistance of a metallic conductor wi...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for equivalent resistance of two resistors connec...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for equivalent resistance of two resistors connec...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for the equivalent emf and internal resistance of...
Text Solution
|