A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-AC CIRCUITS-COMPREHENSION-(II)( Assuming that any resistance of inductor is included in R, answer the following question)
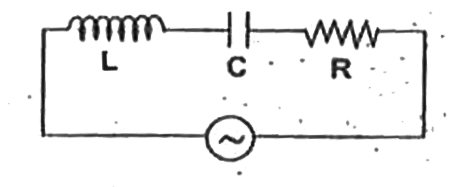
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit shown in the figure is a series LCR circuit connected to a...
Text Solution
|