Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUBHASH PUBLICATION-ANNUAL EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER MARCH 2017-PART D
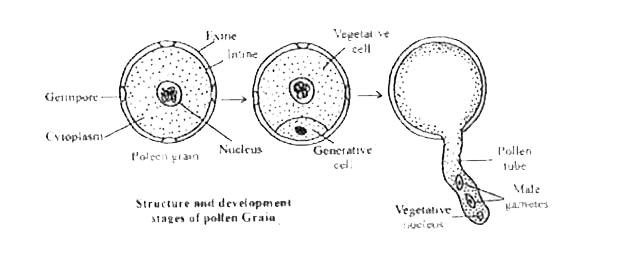
- Explain the structure of pollen grains in Angiosperms.
Text Solution
|
- Draw a neat labelled diagram of human male reproductive system.
Text Solution
|
- Explain mendel's experiment to describe inheritance of one gene with r...
Text Solution
|
- List the salient features of the Human Genome
Text Solution
|
- Name the diseases caused by following organisms : (a) Rhinovirus. (b...
Text Solution
|
- What is Bee - Keeping? Write any four points for a successful Bee - Ke...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the biogas plant with a neat labelled diagram
Text Solution
|
- What is Biopiracy ?
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is Ecological succession? (b) Write types of plant successi...
Text Solution
|
- Explain mutualism with examples.
Text Solution
|
- Write a brief account of electrostatic precipitator with a neat labell...
Text Solution
|