Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
TISSUES
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS (CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER)|10 VideosTISSUES
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS (FILL IN THE BLANKS)|5 VideosTISSUES
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION|Exercise UNIT TEST (ANSWER THE FOLLOWING)|4 VideosTHE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION|Exercise UNIT TEST ( ANSWER THE FOLLOWING )|4 VideosWHY DO WE FALL ILL ?
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION|Exercise UNIT TEST (ANSWER THE FOLLOWING)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CPC CAMBRIDGE PUBLICATION-TISSUES-EXERCISE
- Define tie term "tissue"
Text Solution
|
- How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue ? Name th...
Text Solution
|
- How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants ?
Text Solution
|
- Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the b...
Text Solution
|
- What are the function of the stomata?
Text Solution
|
- Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle...
Text Solution
|
- What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Text Solution
|
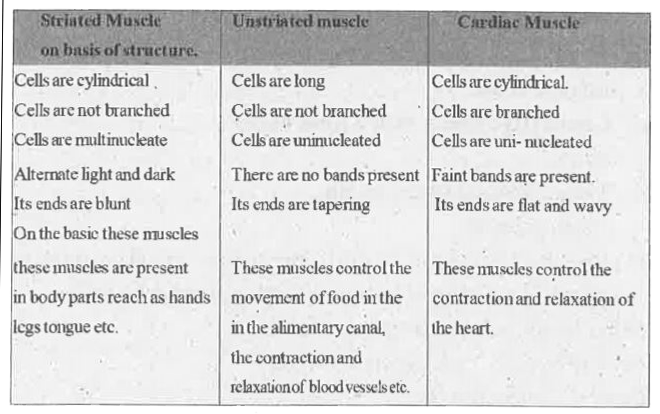
- Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a neat labelled diagram of neuron.
Text Solution
|
- Name the following. (a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our m...
Text Solution
|
- Identity the type of tissue in the following : skin, bark of tree, bon...
Text Solution
|
- Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Text Solution
|
- What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Text Solution
|
- How does the cork act as a protective tissue ?
Text Solution
|
- Complete the table
Text Solution
|