Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
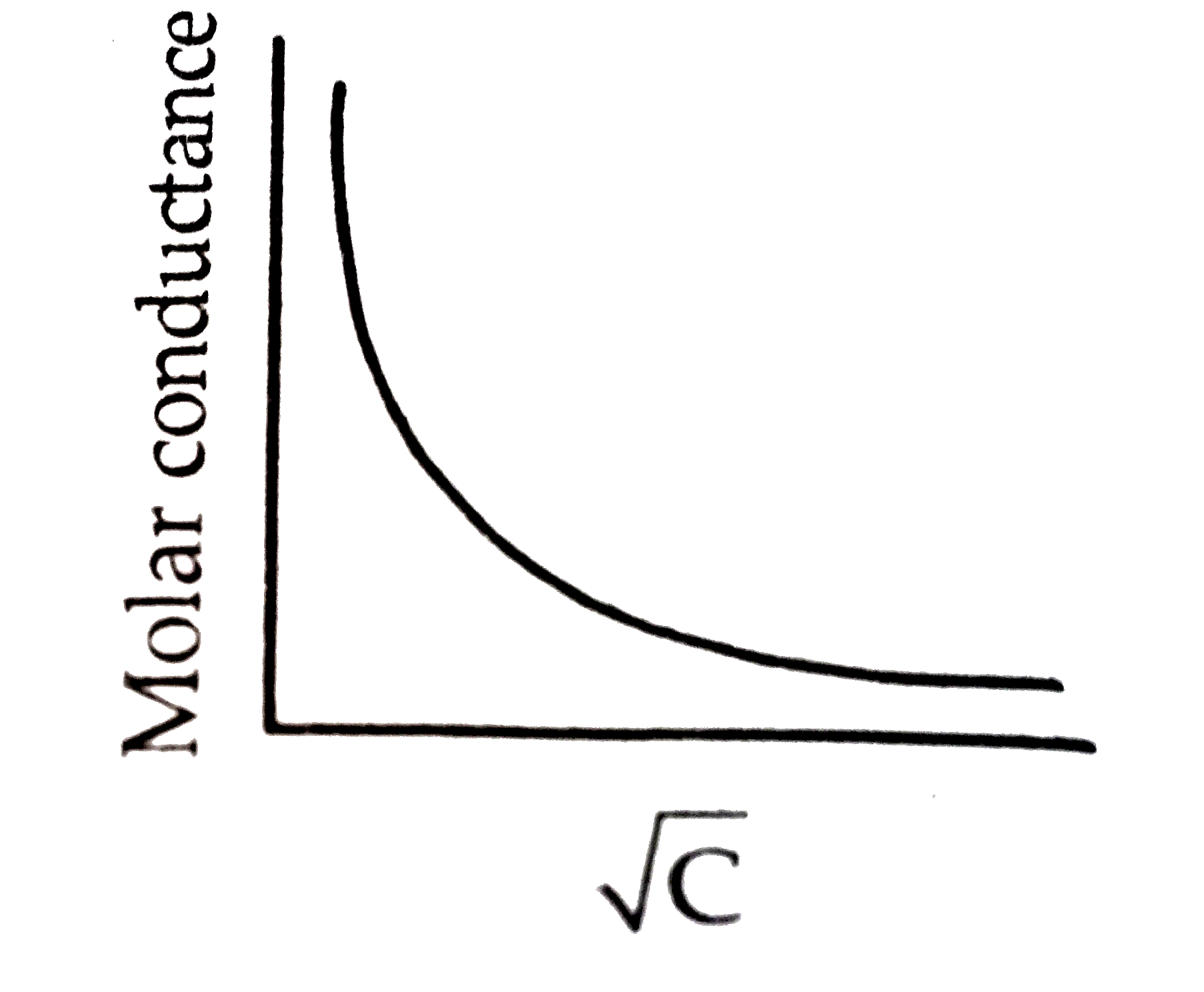
- (a) What is limiting molar conductivity ? Why there is step rise in th...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the e.m.f of the cell Mg(s)//Mg^(2+)(0.1 M)||Cu^(2+)(1.0xx10...
Text Solution
|
- (a) What is limiting molar conductivity ? Why there is step rise in th...
Text Solution
|
- Mg(s) |Mg^(2+) (0.1M)||Cu^(2+) (1xx 10^(-1) M) |Cu(s) सेल के EMF क...
Text Solution
|
- (i) प्रबल तथा दुर्बल विधुत अपघट्यों को उदाहरण द्वारा समझाइए | (ii) ...
Text Solution
|
- The cell reaction of a cell is Mg+Cu^(2+) to Mg^(2+)+Cu (Given E(Mg^(2...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate E("cell")^(@) of the cell Mg|Mg^(2+)||Cu^(+)|Cu Given : E(Mg...
Text Solution
|
- Write the Nernst equation and calculate the e.m.f. of the following ce...
Text Solution
|
- Write the Nernst equation and calcualte emf of the following cell at 2...
Text Solution
|