A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-ELECTRONS & PHOTONS-RECENT COMPETITIVE QUESTIONS
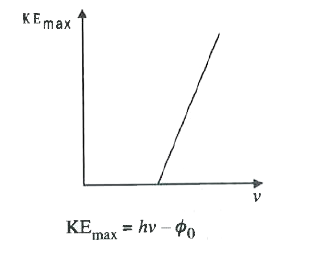
- According to Einstein's photoelectric equation the graph of K.E. of th...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is moving in an orbit of a hydrogen atom from which there ...
Text Solution
|
- v(1) is the frequency of the series limit of Lyman series, v(2) is te ...
Text Solution
|
- The de-Broglie wavelength of the electron in the ground state of the h...
Text Solution
|
- The photoelectric threshold wavelength for silver in lambda(0).The ene...
Text Solution
|
- An electron of mass m(e) and a proton of mass m(p) are moving with the...
Text Solution
|
- Pick out the wrong statement.
Text Solution
|
- A proton and an alpha particle are accelerated through the same potent...
Text Solution
|
- In hydrogen atom , electron excites from ground state of higher energy...
Text Solution
|
- An alpha - particle and a proton moving with the same kinetic energy e...
Text Solution
|
- X- rays, gamma rays and microwaves travelling in vacuum have
Text Solution
|
- If n is the orbit number of the electron in a hydrogen atom , the corr...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle with a velocity 2 xx 10^3 ms^-1 passes undeflected ...
Text Solution
|
- Maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by a metal is 1.8 xx 10^...
Text Solution
|
- lamda(1) and lamda(2) are used to illuminated the slits. beta(1) and b...
Text Solution
|
- What is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron accelerated through ...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons depends on
Text Solution
|
- Find the de-Broglie wavelength of an electron with kinetic energy of 1...
Text Solution
|
- Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1 eV an...
Text Solution
|
- The best waves for emission of electrons from a surface :
Text Solution
|