Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION|Exercise CONTINUOUS EVALUATION (ASSIGNMENT)|4 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION|Exercise PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS|4 VideosDUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION|Exercise PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR SELF ASSESSMENT|5 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITIVE EXAM CORNER|37 VideosELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION|Exercise Competitive Exam Corner|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NEW JOYTHI PUBLICATION-DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER -EVALUATION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
- All the photoelectrons are not emitted with same energy. Give reason.
Text Solution
|
- Light is incident on the cathode of a photocell and the stopping volt...
Text Solution
|
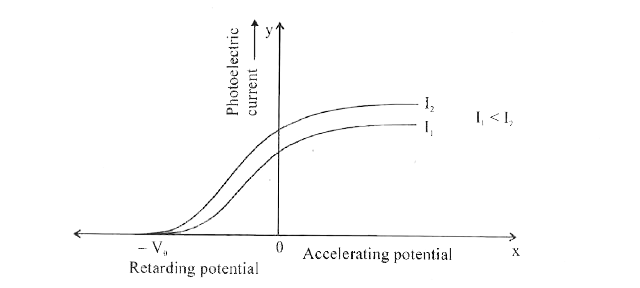
- The graph shows the variation of photoelectric current with accelerati...
Text Solution
|
- Find the effective capacity of the combination shown below :
Text Solution
|
- The above graph shows frequency of an incident photon and maximum kine...
Text Solution
|
- a. What is the purpose of Cu(2)? b. Which plate becomes positive? ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Why de-Broglie wave associated with a moving car is not visible ? ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Give the expression showing the relation between energy and moment...
Text Solution
|
- a. The wave nature of matter is not noticeable in our daily observati...
Text Solution
|
- What do the graphs represent?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are is not correct about a photon?
Text Solution
|
- a. Every metal has a definite work function. Why all photoelectrons ...
Text Solution
|
- Eventhough metals have free electrons, they cannot escape from metal ...
Text Solution
|
- Define 1 eV.
Text Solution
|
- What are the factors on which the rate of thermionic emission depends?
Text Solution
|
- Does photoelectric effect violate the law of conservation of energy?
Text Solution
|
- Give examples for metals sensitive to UV rays and then for visible lig...
Text Solution
|
- Why is photocurrent proportional to intensity?
Text Solution
|
- What is saturation current?
Text Solution
|
- How does a fire alarm work?
Text Solution
|