Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER MARCH 2019-PART-IV
- The force F acting on a body moving in a circular path depends on mass...
Text Solution
|
- State and prove Bernoulli's theorem for a flow of incompressible, non-...
Text Solution
|
- Prove the law of conservation of linear momentum use it to find the re...
Text Solution
|
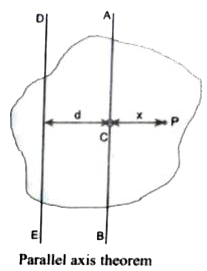
- State and prove parallel axis theorem
Text Solution
|
- What is elastic collision ? Derive an expression for final velocities ...
Text Solution
|
- How will you determine the velocity of sound using resonance air colum...
Text Solution
|
- Derive Mayer's relation for an ideal gas.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the horizontal oscillations of a spring.
Text Solution
|
- Write down the equation of a freely falling body under gravity.
Text Solution
|
- Define orbital velocity and establish an expression for it.
Text Solution
|