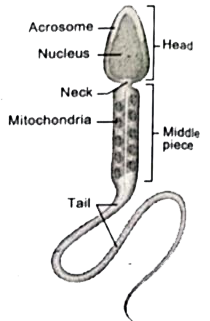
The human sperm is a microscopic, flagellated and motile gamete. The whole body of the sperm is enveloped by plasma membrane and is composed of a head, neck and a tail. The head comprises of two parts namely acrosome and nucleus. Acrosome is a small cap like pointed structure present at the tip of the nucleus and is formed mainly from the Golgi body of the spermatid. It contains hyaluronidase, a proteolytic enzyme, popularly known as sperm lysin which helps to penetrate the ovum during fertilization. The nucleus is flat and oval. The neck is very short and is present between the head and the middle piece. It contains the proximal centriole towards the nucleus which plays a role in the first division .of the zygote and the distal centriole gives rise to the axial filament of the sperm. The middle piece possesses mitochondria spirally twisted around the axial filament called mitochondrial spiral or nebenkem. It produces energy in the form of ATP molecules for the movement of sperms. The tail is the longest part of the sperm and is slender and tapering. It is formed of a central axial filament or axoneme and an outer protoplasmic sheath. The lashing movements of the tail push the sperm forward.