Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMS AND NUCLEI
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|3 VideosATOMS AND NUCLEI
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS|23 VideosATOMS AND NUCLEI
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS|23 VideosBOARD QUESTION PAPER (SOLVED) - 2019
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MBD -HARYANA BOARD-ATOMS AND NUCLEI-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Describe the laws of radioactive decay. Derive equation of radioactive...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain the laws of radioactive disintegration. On its basis...
Text Solution
|
- What are alpha particles ? In the reaction ""(z)X^(A) rarr Y + alpha-p...
Text Solution
|
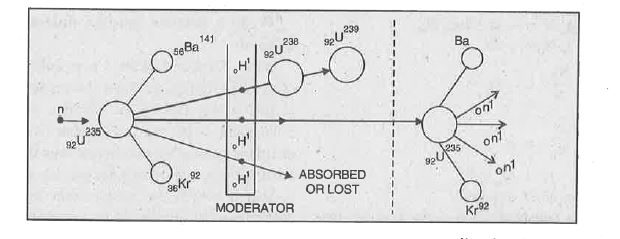
- Define nuclear fission. Write the fission reaction of a neutron with u...
Text Solution
|
- What is the nuclear fission reaction ? Give one example.
Text Solution
|
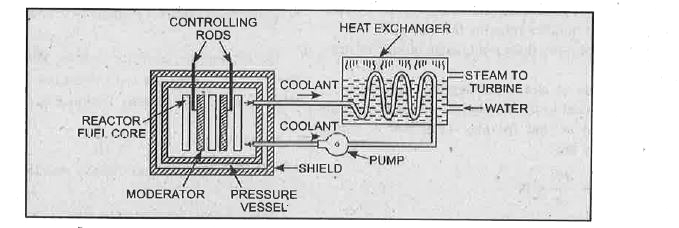
- Draw a labelled diagram of a nuclear reactor and explain the functions...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the function of moderator, control rods and coolant in a nucl...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a simplified diagram showing working of Nuclear Power Plant.
Text Solution
|
- Write a detailed note on nuclear reactor with diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the role of control rods in a reactor. Why are they made of ca...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
Text Solution
|
- Calculate binding energy per n ucleon of ""(83)Bi^(209). Given mass of...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the Rutherford experiment on the scattering of alpha particles...
Text Solution
|
- Uranium ""(92)U^(238) is not suitable for chain reaction . Why ?
Text Solution
|
- How are beta-rays emitted from a nucleus, when it does not contain ele...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss three basic postulates of Bohr's model of atom.
Text Solution
|
- What are important features of J.J. Thomson's atom model ? Why was it ...
Text Solution
|
- What is nuclear fission ? Give an example to illustrate it. What is th...
Text Solution
|
- Explain Nuclear fission reaction with an example.
Text Solution
|
- What is the basic nuclear process underlying beta^(-) decay ? Write nu...
Text Solution
|