A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (ASSERTION REASON TYPE QUESTIONS)|10 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS)|3 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (C. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|25 VideosNUCLEI
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|15 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS METERIALS DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (D. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)
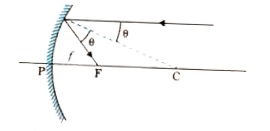
- Rays parallel to principal axis, incident on the spherical mirror at d...
Text Solution
|
- Rays parallel to principal axis, incident on the spherical mirror at d...
Text Solution
|
- Rays parallel to principal axis, incident on the spherical mirror at d...
Text Solution
|
- Focal lengths of objective and eyepiece of a compound microscope are 1...
Text Solution
|
- Focal lengths of objective and eyepiece of a compound microscope are 1...
Text Solution
|