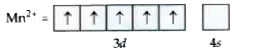
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THE D-AND F-BLOCK ELEMENTS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION A ) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (CHOOSE THE CORRECT OPTION)|7 VideosTHE D-AND F-BLOCK ELEMENTS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-I (3 marks each)|22 VideosSURFACE CHEMISTRY
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST ( SECTION A)|7 VideosTHE P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST ( SECTION A)|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-THE D-AND F-BLOCK ELEMENTS -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-II (5 marks each)
- (a) Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series : Ti^(4+),V...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Account for the following : (i) Mn shows the highest oxidation s...
Text Solution
|
- The elements of 3d transition series are given as : Sc Ti V Cr M...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Blackish brown coloured solid (A) which is an oxide of manganese, ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Account for the following: (i) Ce^(4+) is a strong oxidising age...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How will you prepare : (i) K(2)MnO(4) from MnO(2) ? (ii) Na(2)...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Complete the following equations : (i) Cr(2)O(7)^(2-)+2OH^(-)to ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Name the element of 3d transition series which shows maximum numbe...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Give reasons for the following: (i) Mn^(3+) is a good oxidising ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Complete the following chemical equations : (i) MnO(4)^(-)(aq)+S...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Complete the following chemical equations : (i) Cr(2)O(7)^(2-)(a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) (i) Which is stronger reducing agent Cr^(2+) or Fe^(2+) and why? ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the following: (a) Actinoids show large number of oxidation ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Account for the following : (i) Oxidising power in the series VO...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Out of Ag(2)SO(4),CuF(2),MgF(2) and CuCl, which compound will be c...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following: (a) Transition metals have high enth...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In the titration of FeSO(4) with KMnO(4) in the acidic medium, why...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write balanced equations to represent what happens when (i) Cu^(...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Transition metals can act as catalysts because these can change th...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the standard electrode potential values (M2+/M) of the elemen...
Text Solution
|