Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-1(LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|7 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-1(NUMERICAL PROBLEMS)|9 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-1(SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-1)|11 VideosNUCLEI
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC -2 (Numerical Problems)|3 VideosSample Paper 1
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise|36 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OSWAAL PUBLICATION-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-TOPIC-1(SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-2)
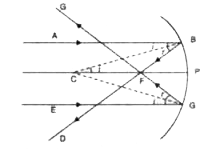
- Derive the relation f = R//2 in the case of a concave mirror.
Text Solution
|
- A point object O is kept at a distance of 30cm from a convex lenx of p...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 20cm is places coaxially with a convex ...
Text Solution
|
- Your are given three lenses L(1), L(2) and L(3) each of focal length 2...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens made up of glass of refractive index 1.5 is dipped, in t...
Text Solution
|
- Use the mirror equation to show that (a) An object placed between f ...
Text Solution
|