Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ATOMS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS|30 VideosATOMS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise FILL IN THE BLANKS.|13 VideosATOMS
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL EXERCISES|8 VideosALTERNATING CURRENT
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION -C)|2 VideosCBSE EXAMINATION PAPER 2020
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION D|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-ATOMS-CASE BASED/SOURCE - BASED INTERGRATED QUESTIONS
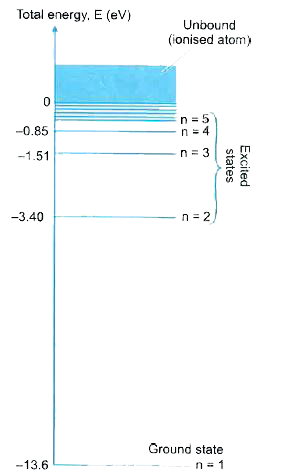
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|
- Read the pasage given below as well as the adjoining energy level di...
Text Solution
|