Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT ENGLISH-QUADRILATERALS-Exercise 8.2
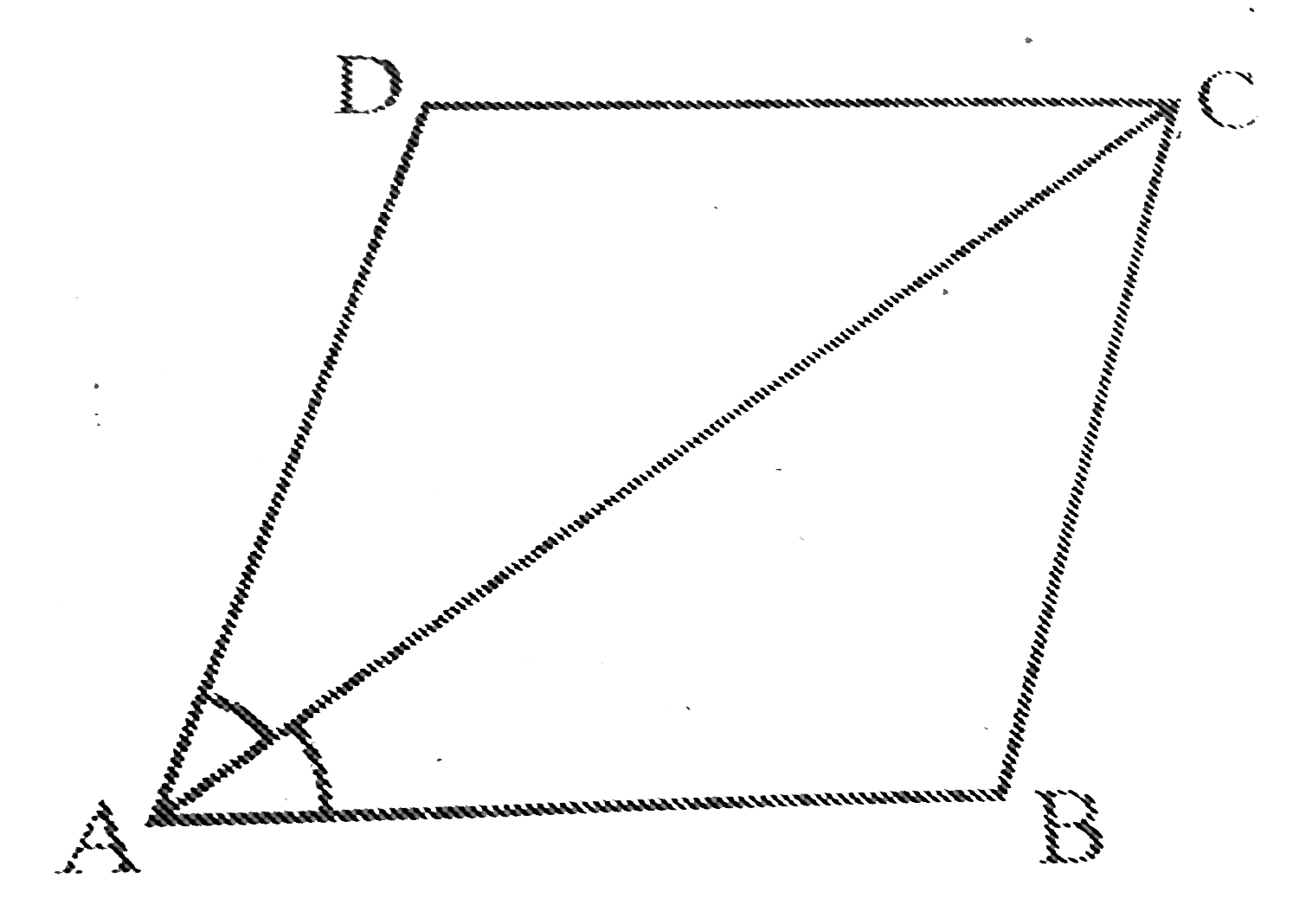
- Diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD bisects \ /A. Show that (i) it bi...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a rectangle and P, Q, R and S are mid-points of the sides AB,...
Text Solution
|
- P, Q, R and S are respectively the mid-points of the sides AB, BC, CD ...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a quadrilateral in which P, Q, R and S are mid-points of the...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is a triangle right angled at C. A line through the mid-point M ...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the line segments joining the mid-points of the opposite s...
Text Solution
|
- In a parallelogram ABCD, E and F are the mid-points of sides AB and C...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a trapezium in which A B\ ||\ D C, BD is a diagonal and E is ...
Text Solution
|