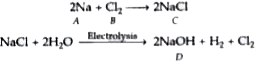Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-METALS AND NON METALS-LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- An element A burns with golden flame in air. It reacts with another el...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Describe an activity to show that metals are good conductors of el...
Text Solution
|
- (a) When calcium metal is added to water, the gas evolved does not cat...
Text Solution
|
- In the formation of a compound XY2, atom X donates one electron to eac...
Text Solution
|
- Give reasons for the following: (i) Ionic compounds have generally hi...
Text Solution
|