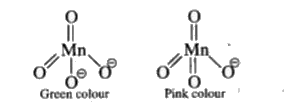
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
METALLURGY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-1 (MATCH THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS)|2 VideosMETALLURGY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-1 (Integer answer type Questions)|6 VideosMETALLURGY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-1 (PASSAGE-I)|3 VideosIONIC EQUILLIBRIUM
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise ADDITIONAL PRACTICE EXERCISE (PRACTICE SHEET ( ADVANCED))|11 VideosNITROGEN CONTAINING COMPOUNDS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise Conversions|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems