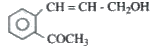A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PRACTICAL CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-3 (Linked Comprehension type questions)|6 VideosPRACTICAL CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-3 (Match the following questions)|2 VideosPRACTICAL CHEMISTRY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise PRACTICE SHEET-3 (Single answer questions)|7 VideosPOLYMERS
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise OBJECTIVE EXERCISE - 4|59 VideosPRINCIPLES OF METALLURGY
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise SUBJECTIVE EXERCISE-2 (LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS )|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-PRACTICAL CHEMISTRY-PRACTICE SHEET-3 (More than one correct answer Questions)
- An organic compound containing one oxygen gives red colour with cerric...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following radicals will be precipitated by passing H(2)S ...
Text Solution
|
- On being heated with conc. HNO(3) and ammonium molybdate solution, the...
Text Solution
|
- The reagent NH(4)CI and aqueous NH(3) precipitates:
Text Solution
|
- Some salts which give brown vapours with conc, H(2)SO(4) may be :
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following will respond to positive chromyl chloride test?
Text Solution
|
- Which is ( are ) insoluble in water ?
Text Solution
|
- KCN is used for separting
Text Solution
|
- Which will not give test of Fe^(3+) ions ?
Text Solution
|