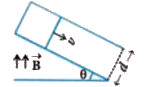
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - (D NCERT Exemplar Solution) (Very Short Answer Type Questions|6 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION - (D NCERT Exemplar Solution) (Short Answer Type Questions|5 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION -C (Objective Questions) (VSQs) Assertion and Reason Type Questions|7 VideosMACHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER|11 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise QUESTION PAPER|11 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS -SECTION - (D NCERT Exemplar Solution)
- A rod of mass m and resistance R slides smoothly over two parallel con...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following diagrams does not represent a streamline flow ?
Text Solution
|
- Along a streamline …….
Text Solution
|
- An ideal fluids flows through a pipe of circular cross -section made o...
Text Solution
|
- The angle of contact at the interface of water glass is 0^(@) ethylal...
Text Solution
|
- For a surface molecule ……..
Text Solution
|
- Pressure is a scalar quantity because …….
Text Solution
|
- A wooden block with a coin placed on its top, floats in water as shown...
Text Solution
|
- With increases in temperature the viscosity ………
Text Solution
|