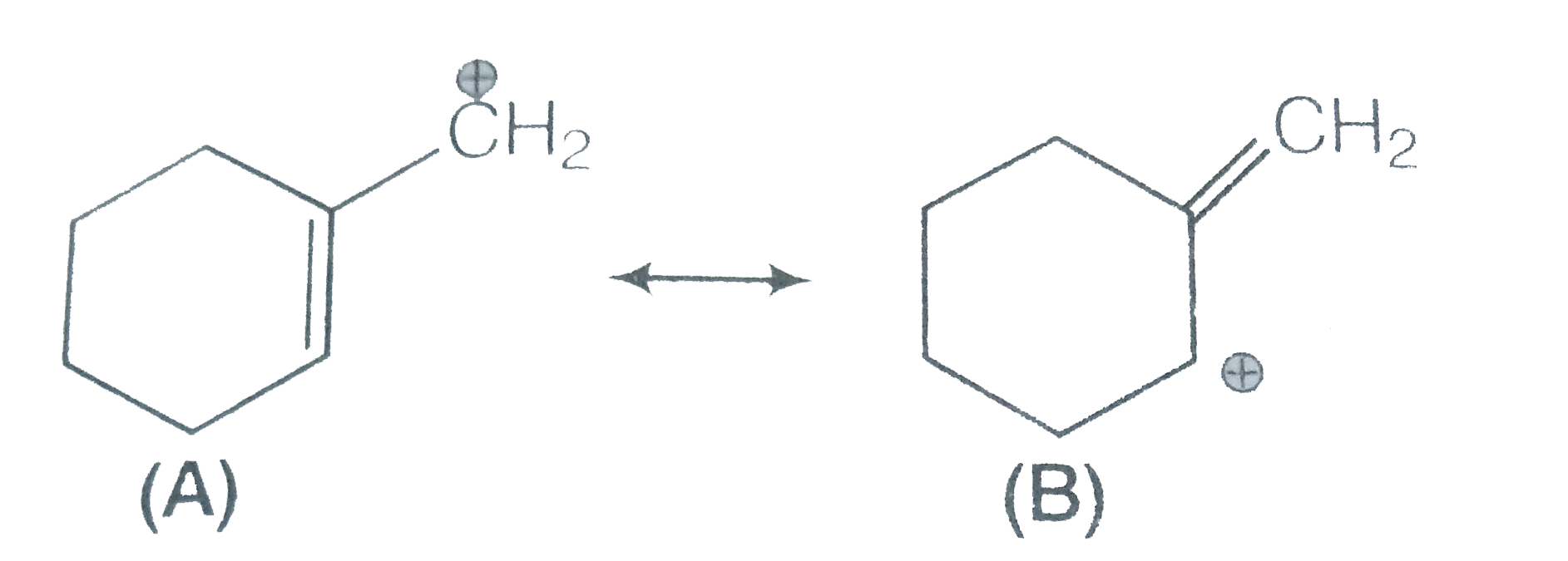
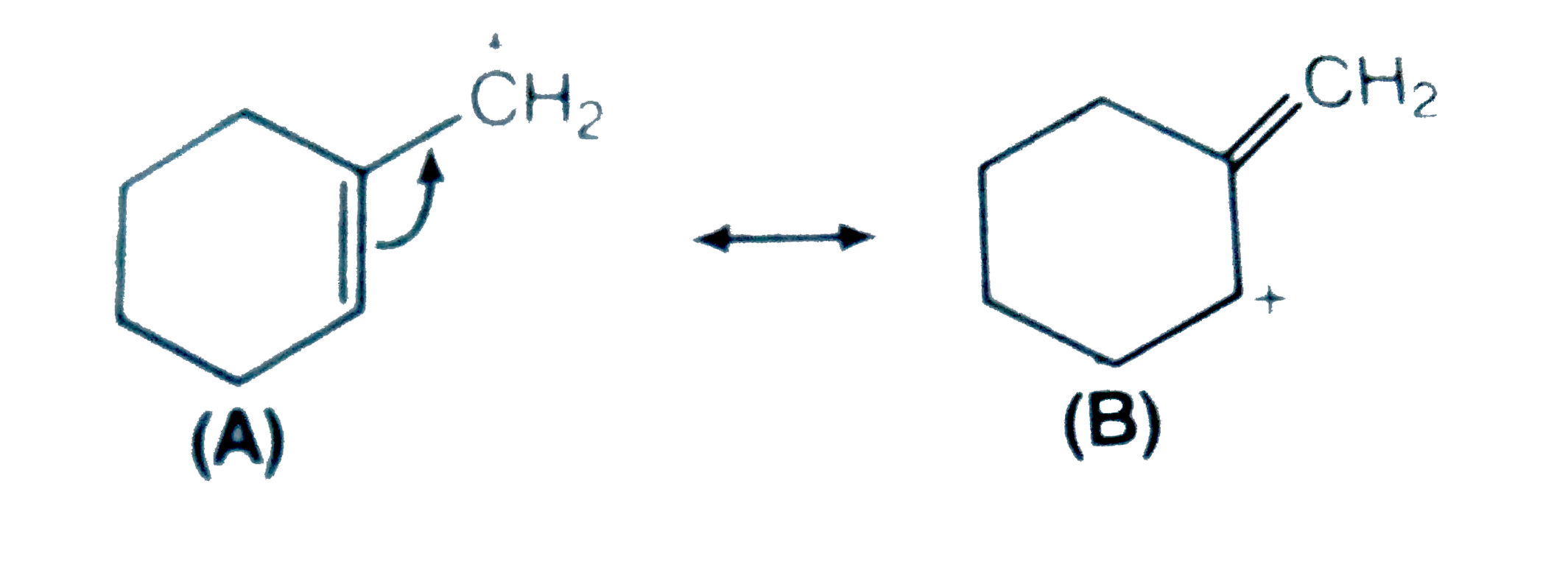
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Matching the columns|5 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Assertion and Reason|6 VideosORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer type question|6 VideosHYDROGEN
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|8 VideosREDOX REACTIONS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES-Short Answer type question
- Show the polarisation of carbon-magnesium bond in the following struct...
Text Solution
|
- Compounds with same molecular formula but differing in their structure...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following selected chains is correct to name to given com...
Text Solution
|
- In DNA and RNA, nitrogen atom is present in the ring system. Can Kjeld...
Text Solution
|
- If a liquid compound decomposes at its boiling point, which method (s)...
Text Solution
|
- 'Stability of carbocations depends upon the electron releasing inducti...
Text Solution
|
- 'Stability of carbocations depends upon the electron releasing inducti...
Text Solution
|
- 'Stability of carbocations depends upon the electron releasing inducti...
Text Solution
|
- 'Stability of carbocations depends upon the electron releasing inducti...
Text Solution
|
- Three students, Manish, Ramesh and Rajini were determining the extra e...
Text Solution
|
- Name the compounds whose line formula are given below.
Text Solution
|
- Write structural formulae for compounds named as (a) 1-bromoheptane ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the resonance structures of the following compounds. (a) CH(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the most stable species in the following set of ions giving r...
Text Solution
|
- Given three points of differences between inductive effect and resonan...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will not exist as resonance hybrid. G...
Text Solution
|
- Why does SO(3) act as an electrophile ?
Text Solution
|
- Resonance structures of propenal are given below. Which of these reson...
Text Solution
|
- By mistake, an alcohol(boiling point 97^(@)C) was mixed with a hydroca...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the two structures (A) and (B) given below is more stabilised...
Text Solution
|