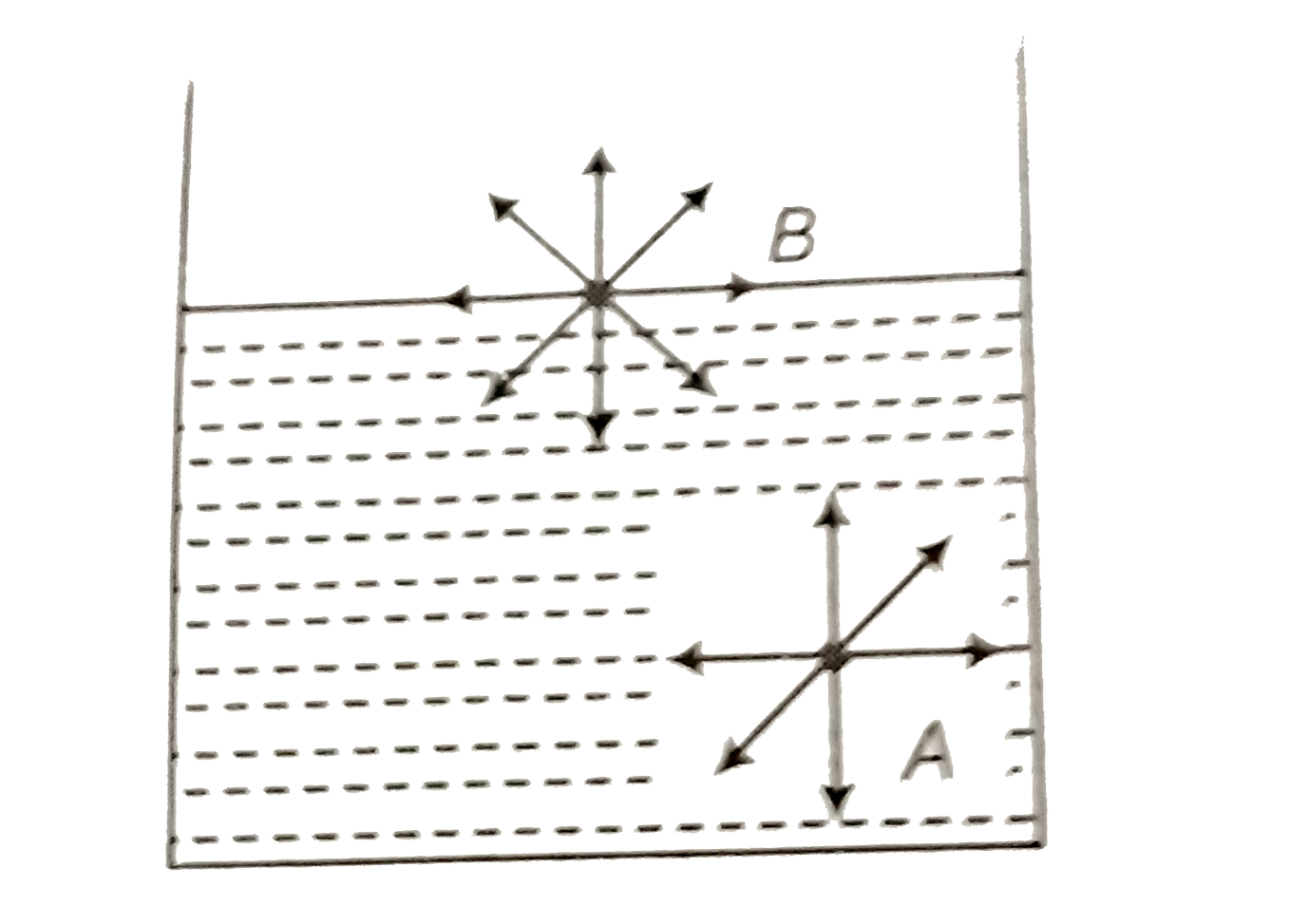
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Very Short Answer Type Questions|5 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Short Answer Type Questions|5 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long Answer Type Questions|3 VideosLAWS OF MOTION
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise Long answer Type Questions|9 VideosMECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
NCERT EXEMPLAR ENGLISH|Exercise LONG SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems