Compressibility factor (Z) : Deviation between real gas and idea gas is known as compressibility factor (Z).
`Z=(pV)/(nRT) " "` …..(Eq. -i)
where, Z = 1
Z = Compressibility factor of ideal gas deviation behaviour,
`Z =(V_("real"))/(V_("ideal"))=("real molar volume")/("ideal molar volume")` .......(constant T)
For `Z = 1, Z gt 1, Z lt 1` is give in points (i), (ii), (iii)
(i) Z = 1 OR 1 deviation factor :
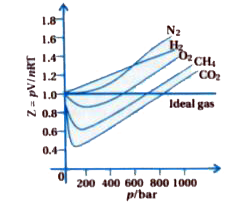
For ideal gas Z = 1 at all temperature and pressure , because pV = nRT.
If Z = 1 then gas is ideal gas and `Z to p` graph is parallel line.
At very low pressures all gases shown have Z = 1 and behave as an ideal gas.
Ideal gas law, follow at Z = 1 at Boyle temperature of Boyle point at real pressure.
(ii) `Z gt 1` OR Positive deviation :
At high pressure all real gases shows `Z gt 1` they are less compressible than ideal gas. If `Z gt 1` than permanently gas.
`N_(2), H_(2)O_(2)` shows positive deviation, `Z to p` graph show positive deviation.
According to diagram for `H_(2)` gas at high pressure `Z gt 1`. When pressure increases value of Z becomes more positive.
Ideal gas shows positive deviation of higher than Boyle.s point and value of a are higher than are then intermolecular attraction force are weak.
(iii) `Z lt 1` OR negative deviation :
At intermediate pressure, most gasses have `Z lt 1`.
For `O_(2), CH_(4), CO_(2)` gas shows negative deviation, `Z to p` graph shows negative deviation.
According to diagram, `Z lt 1` at lower pressure. Initially pressure increases than Z decreases, after that z cross ideal gas line.
At lower temperature then Boyle.s point value of Z decreases at increases pressure, which reacted at minimum value and pressure is continuously increases.
(iv) Graph between `Z to p` for some gases :
(v) Relation between Z real gas and ideal molar volume :
`Z = (pV_("real"))/(nRT) " "` .....(Eq. -i)
If gas is an ideal,
`V_("real")=(nRT)/(p) " "` ......(Eq. -iii)
Value of `(nRT)/(p)` is put in (iv) then we get equation (iii).
`Z=(V_("real"))/(V_("ideal")) " "` ....(Eq. -v)
`therefore Z =("Real molar volume")/("Ideal molar volume")` ......(constant T)
..Compressibility factor is ratio of real molar volume and ideal molar volume...
