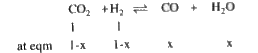A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A mixture of one mole of CO(2) and one mole of H(2) attains equilibriu...
Text Solution
|
- A mixture of one mole of CO(2) and "mole" of H(2) attains equilibrium ...
Text Solution
|
- The partial pressure of CH(3)OH((g)) , CO((g)) and H(2(g)) in equilibr...
Text Solution
|
- At a certain temperature , the equilibrium constant (K(c)) is 4//9 for...
Text Solution
|
- K(c ) for CO(g)+H(2)O(g) hArr CO(2)(g)+H(2)(g) at 986^(@)C is 0.63. A ...
Text Solution
|
- At 675 K, H(2)(g) and CO(2)(g) react to form CO(g) and H(2)O(g), K(p) ...
Text Solution
|
- For the equilibrium H(2)(g)+CO(2)(g)hArr hArr H(2)O(g)+CO(g), K(c)=16 ...
Text Solution
|
- At a given temperature, Ke is 4 for the reaction H(2(g)) + CO(2(g)) hA...
Text Solution
|
- The equilibrium constant for the reaction , H(2) (g) + CO(2) (g) hAr...
Text Solution
|