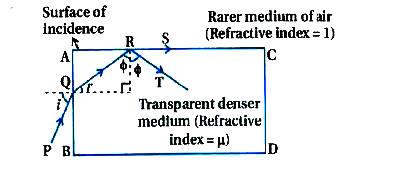Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))(MCQs FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK)|26 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-D (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs))(MCQs FROM .DARPAN. BASED ON TEXTBOOK)(REFRACTION)|32 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)|6 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION D (MCQs ASKED IN COMPETITIVE EXAMS)|34 VideosSAMPLE QUESTION PAPER
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PART-B SECTION-C|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-SECTION-C (NCERT EXEMPLAR SOLUTION) (LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESITONS)
- Show that for a material with refractive index mu ge sqrt(2)~ , light ...
Text Solution
|
- The mixture a pure liquid and a solution in long vertical column (i.e,...
Text Solution
|
- If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interation ca...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusual exotic m...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (O) (...
Text Solution
|