Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at temperature of 623K and a pressure of 300atm. However the rate of reaction can be increased by presence of certain groups in benzene ring. What will be the order of reactivity of following compounds towards the above substitution reaction?
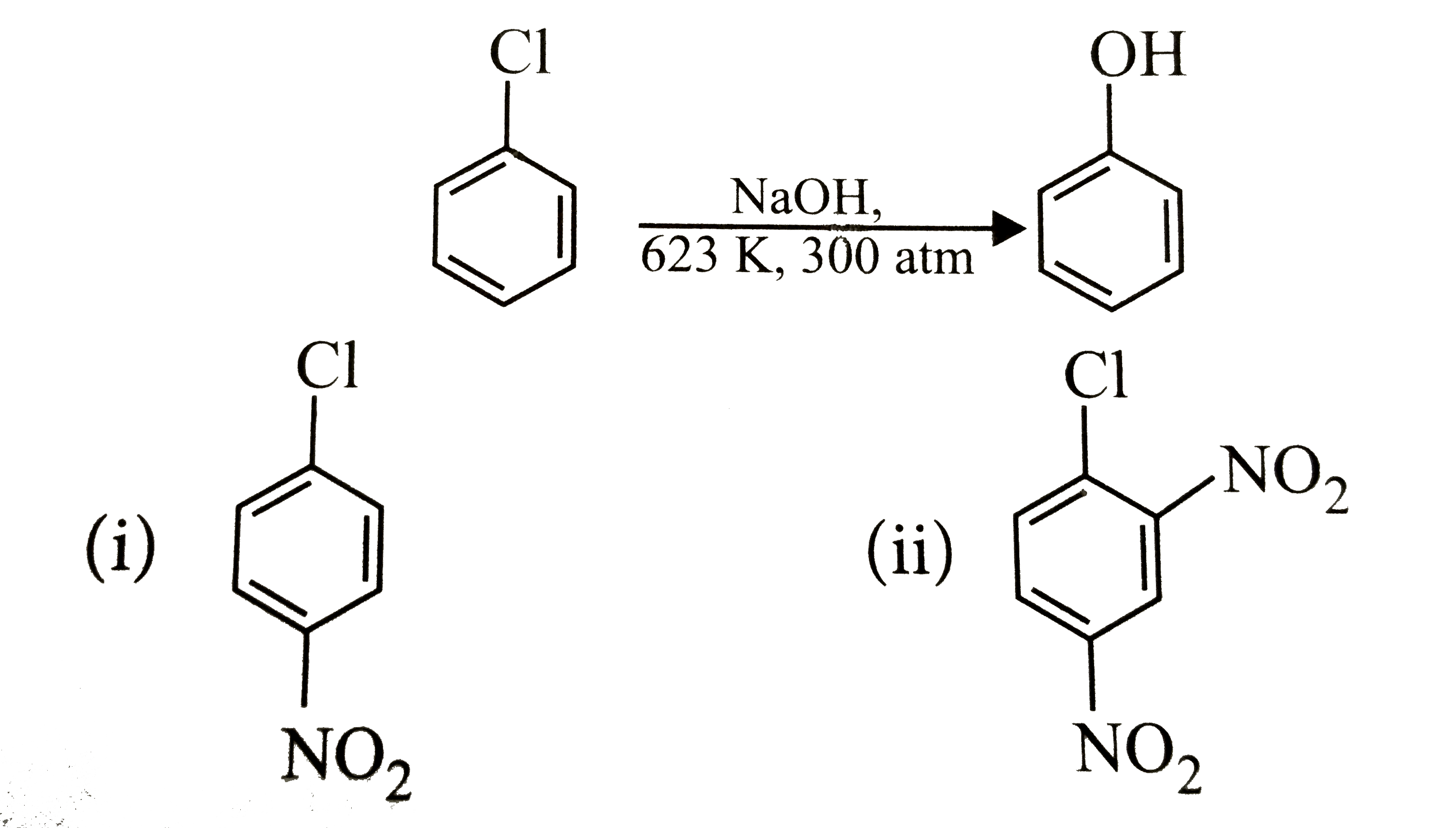
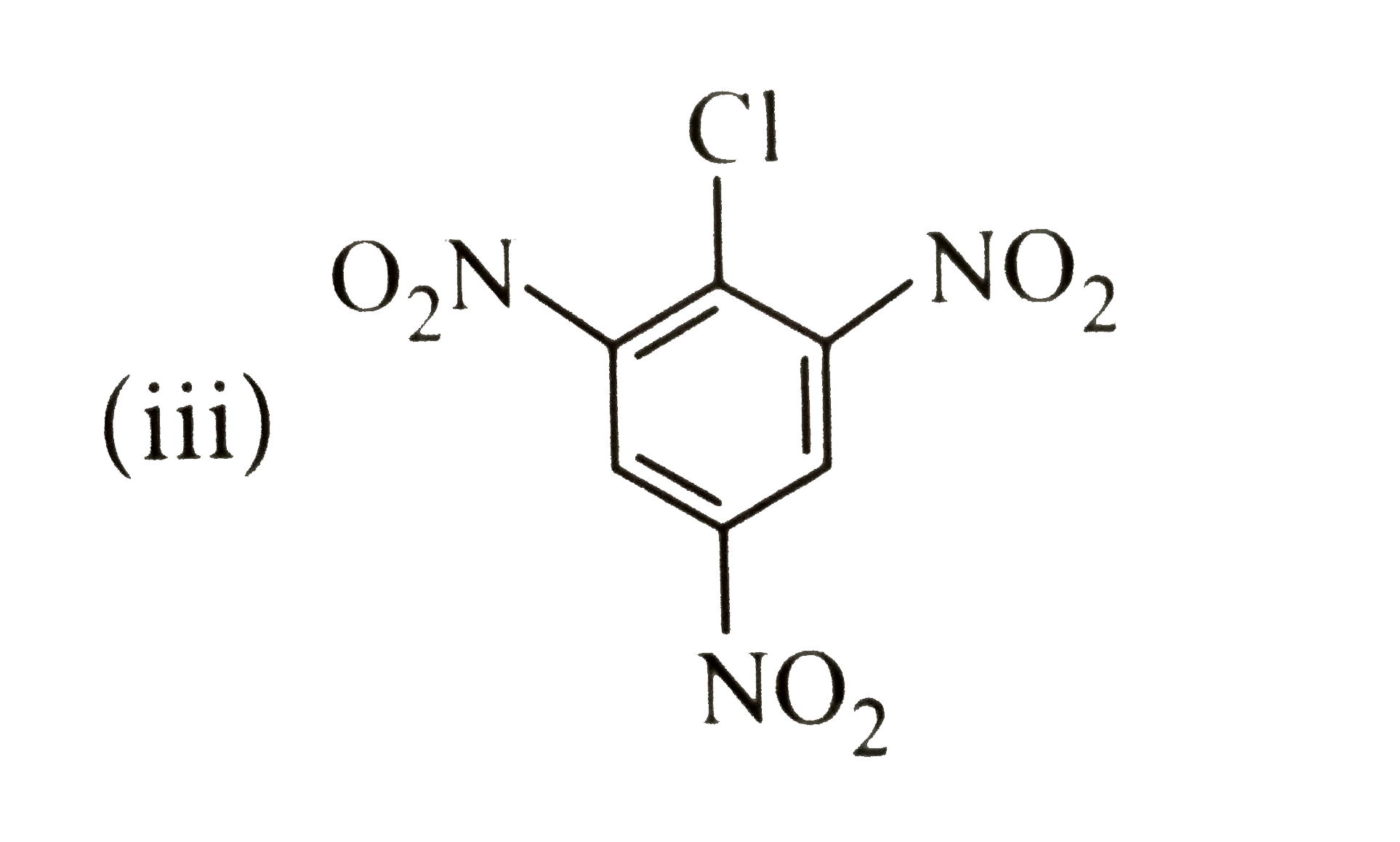
Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at temperature of 623K and a pressure of 300atm. However the rate of reaction can be increased by presence of certain groups in benzene ring. What will be the order of reactivity of following compounds towards the above substitution reaction?




A
(iii)gt(ii)gt(i)
B
(ii)gt(iii)gt(i)
C
(i)gt(ii)gt(iii)
D
(i0gt(iii)gt(ii)
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
A
The presence of an electron withdrawing group `(-NO_2)` at ortho and para -positions increases the reactivity fo haloarenes.
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Free enegry , G = H - TS , is state function that indicates whther a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous. If you think of TS as the part of the system's enegry that is disordered already, then (H -TS) is the part of the system's energy that is still ordered and therefore free to cause spontaneous change by becoming disordered. Also, DeltaG = DeltaH - T DeltaS From the second law of thermodynamics, a reaction is spontaneous if Delta_("total")S is positive, non-spontaneous if Delta_("total")S is negative, and at equilibrium if Delta_('total")S is zero. Since, -T DeltaS = DeltaG and since DeltaG and DeltaS have opposite sings, we can restate the thermodynamic criterion for the spontaneity of a reaction carried out a constant temperature and pressure. IF DeltaG lt 0 , the reaction is spontaneous. If DeltaG gt 0 , the reaction is non-spontaneous. If DeltaG = 0 , the reaction is at equilibrium. Read the above paragraph carefully and answer the following questions based on the above comprehension. One mole of ice si converted to liquid at 273 K, H_(2)O(s) and H_(2)O(l) have entropies 38.20 and 60.03 J mol^(-1) dg^(-1) . Enthalpy change in the conversion will be
Give the decreasing order of the relative reactivity towards SE reaction of the following compounds. a. I. Benzene, II. Phenol, III. Aniline, IV. Chlorobenzene
The typical reaction of benzene and other aromatic compounds are electrophilic substitution. Presence of electron donating group activates the ring towards electrophilic substitution, while presence of electron withdrawing group deactivates the ring towards electrophilic substituion but at the same time activates the ring towards nucleophilic subsituion. Some groups are predominantly meta-directing and all of these are deactivating. Except halogen, most of the o- and p- directing groups are activating groups. Which of the following compound is not formed. X represents mixture of organic compounds. The mixture does not contain
Phenols are more acidic than aliphatic alcohols acidity of phenols can be further increased by the introduction of electron withdrawing groups in aromatic ring .Acidic nature of phenol is because of the resonance stabilization of phenoxide ion Consider the following reactions major product the above reaction would be
Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have K_(a) value of about 10^(-10) , and are tremondously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stablities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring. Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of reasonance is therefore to stablise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make K_(a) larger than for an alcohol. Correct order of acidity is
Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have K_(a) value of about 10^(-10) , and are tremondously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stablities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring. Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of reasonance is therefore to stablise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make K_(a) larger than for an alcohol. Which of the following is strongest acid?
Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have K_(a) value of about 10^(-10) , and are tremondously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stablities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring. Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of reasonance is therefore to stablise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make K_(a) larger than for an alcohol. Which of the following is more stable:
Phenols are converted into their salts by aqueous NaOH but not by aqueous bicarbonates. The salts are converted into the free phenols by aqueous mineral acids, carboxylic acid or carbonic acids. Most phenols have K_(a) value of about 10^(-10) , and are tremondously more acidic than alcohols. The difference in acidity are due to difference in stablities of reactants and products. Phenol and phenoxide ions contain benzene ring and therefore must be hybrid of Kekuley structures Being basic, oxygen can share more than a pair of electron with the ring. Since energy must be supplied to separate opposite charge, the structure of phenols should contain more energy. The net effect of reasonance is therefore to stablise the phenoxide ion to a greater extent than the phenol and thus to shift the equilibrium towards ionization and make K_(a) larger than for an alcohol. Consider the following curves:
Recommended Questions
- Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodi...
Text Solution
|
- what is the correct order of the reactivity of the following compounds...
Text Solution
|
- क्लोरोबेन्जीन की बेन्जीन रिंग की एक प्रतिस्थापन अभिक्रिया का समीकरण लि...
Text Solution
|
- Chlorobenzene can be converted into phenol by heating in aqueous sodiu...
Text Solution
|
- The increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards ...
Text Solution
|
- The increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards ...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reactio...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reactio...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following compound in the descending order of their reacti...
Text Solution
|