Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIN WITH ANSWERS|15 VideosELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise PRACTICAL SKILL BASED QUESTION WITH ANSWERS|20 VideosELECTRICITY
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (Choose the correct option from those given below each question: )|55 VideosMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT
KUMAR PRAKASHAN|Exercise VALUE BASED QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
KUMAR PRAKASHAN-ELECTRICITY-OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (Answer the following questions as directed (Miscellaneous):)
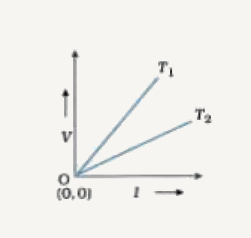
- The voltage - current (V-1) graphs for a metallic conductor at two dif...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of given length is doubled on itself and this process is repeat...
Text Solution
|
- Through which of the following two wires, does the electric current fl...
Text Solution
|
- 400 J of heat is produced in 4 s in a 4.0ohm resistor. Find the potent...
Text Solution
|
- What is the commercial unit of electrical energy?
Text Solution
|
- On what principle is an electric bulb based?
Text Solution
|
- In a circuit, two resistors of resistances 5 Omega and 10 Omega are co...
Text Solution
|
- Write the reletion between resistance R of the filament of a bulb, its...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following bulbs has more resistance? (a) A 220V, 100W b...
Text Solution
|
- Find the minimum resistance that can be made using five resistors, eac...
Text Solution
|
- How does the resistance (R) of a wire depend upon its radius (r)?
Text Solution
|
- An ammeter has a range (0 - 3A) and there are 30 divisions on its scal...
Text Solution
|
- In a voltmeter there are 20 divisions between 0 mark and 0.5 V mark....
Text Solution
|
- To verify the Ohm.s law a circuit diagram was drawn by a student as sh...
Text Solution
|
- Four students connect 4 cells of 1.5 V each to get a battery of voltag...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is correct? (a) one volt is one j...
Text Solution
|
- Keeping the resistance constant, the potential difference applied acro...
Text Solution
|
- Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit...
Text Solution
|
- A potential difference of 10 V is needed to make a current of 0.02 A f...
Text Solution
|
- A current of 200 mA flows through a 4 kOhm resistor. What is the poten...
Text Solution
|