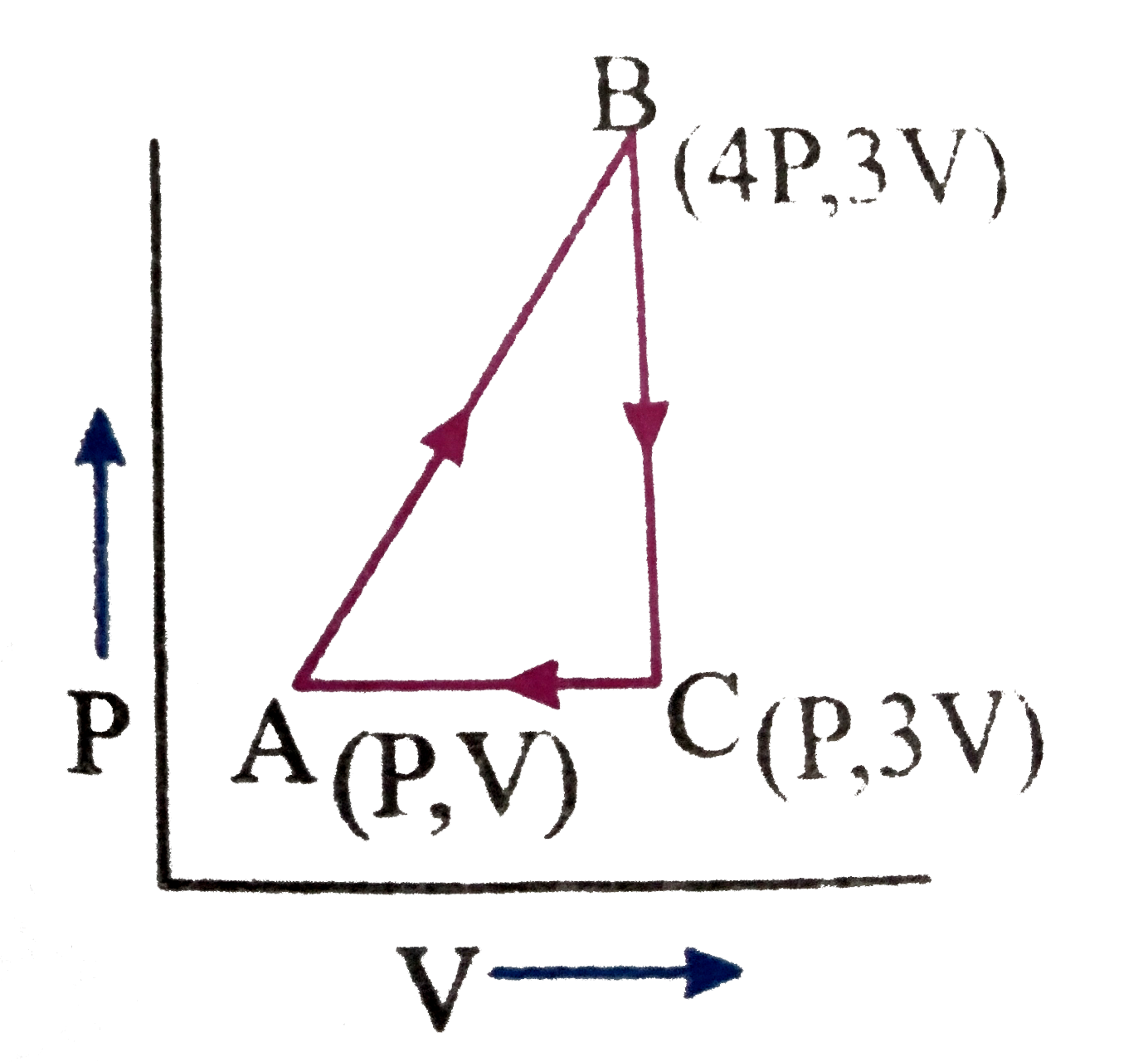
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise 16|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise 17|1 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise 14|3 VideosSUPERPOSITION AND STANDING WAVES
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension Type|5 VideosTRANSMISSION OF HEAT
CENGAGE PHYSICS ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems