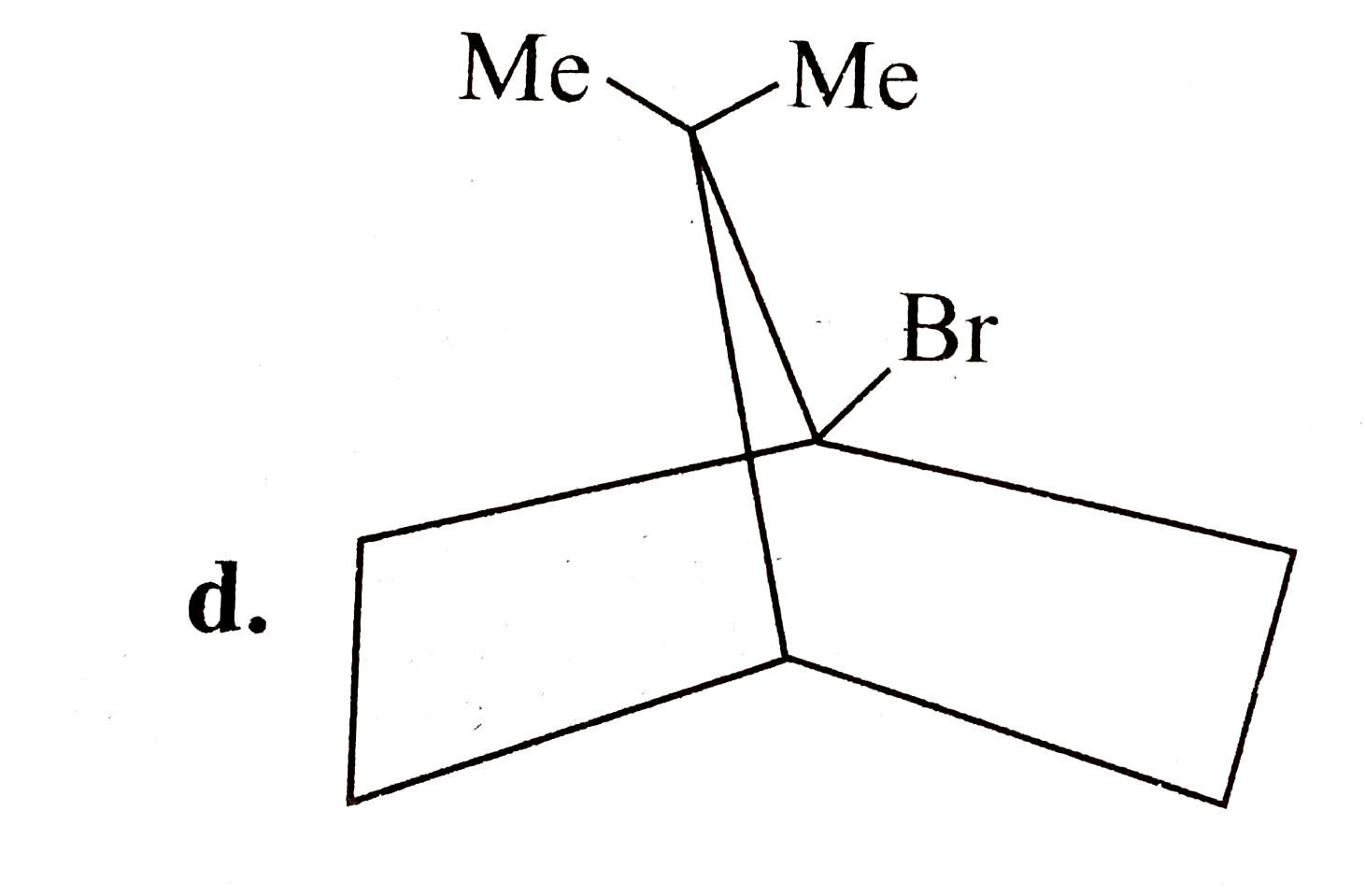
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Multiple Correct|30 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Single correct|43 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Subjective|19 VideosNCERT BASED EXERCISE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Chemical Equilibrium|73 VideosP-BLOCK GROUP 13 - BORON FAMILY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise Archives (Subjecive)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY ENGLISH-ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM-Comprehension
- Which statement is correct ?
Text Solution
|
- The leaving group is that functional group which is ejected with overl...
Text Solution
|
- The leaving group is that functional group which is ejected with overl...
Text Solution
|
- The leaving group is that functional group which is ejected with overl...
Text Solution
|
- The leaving group is that functional group which is ejected with overl...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is wrong ?
Text Solution
|
- The rate of SN^2 reaction depends on the effectiveness of the nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of SN^2 reaction depends on the effectiveness of the nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- The rate of SN^2 reaction depends on the effectiveness of the nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is wrong in the formation of (B) from (A).
Text Solution
|
- Which is correct in the formation of (C) from (A) ?
Text Solution
|
- Which statement is wrong in the formation of (C) from (A) ?
Text Solution
|
- In elimination reaction, the major product is either Saytzeff (more-su...
Text Solution
|
- In elimination reaction, the major product is either Saytzeff (more-su...
Text Solution
|
- In elimination reaction, the major product is either Saytzeff (more-su...
Text Solution
|
- In elimination reaction, the major product is either Saytzeff (more-su...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions : Which of the following are ste...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions : Which of the following regiose...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions : Syn-addition takes place in :
Text Solution
|
- Consider the following reactions : Anti-addition takes place in :
Text Solution
|