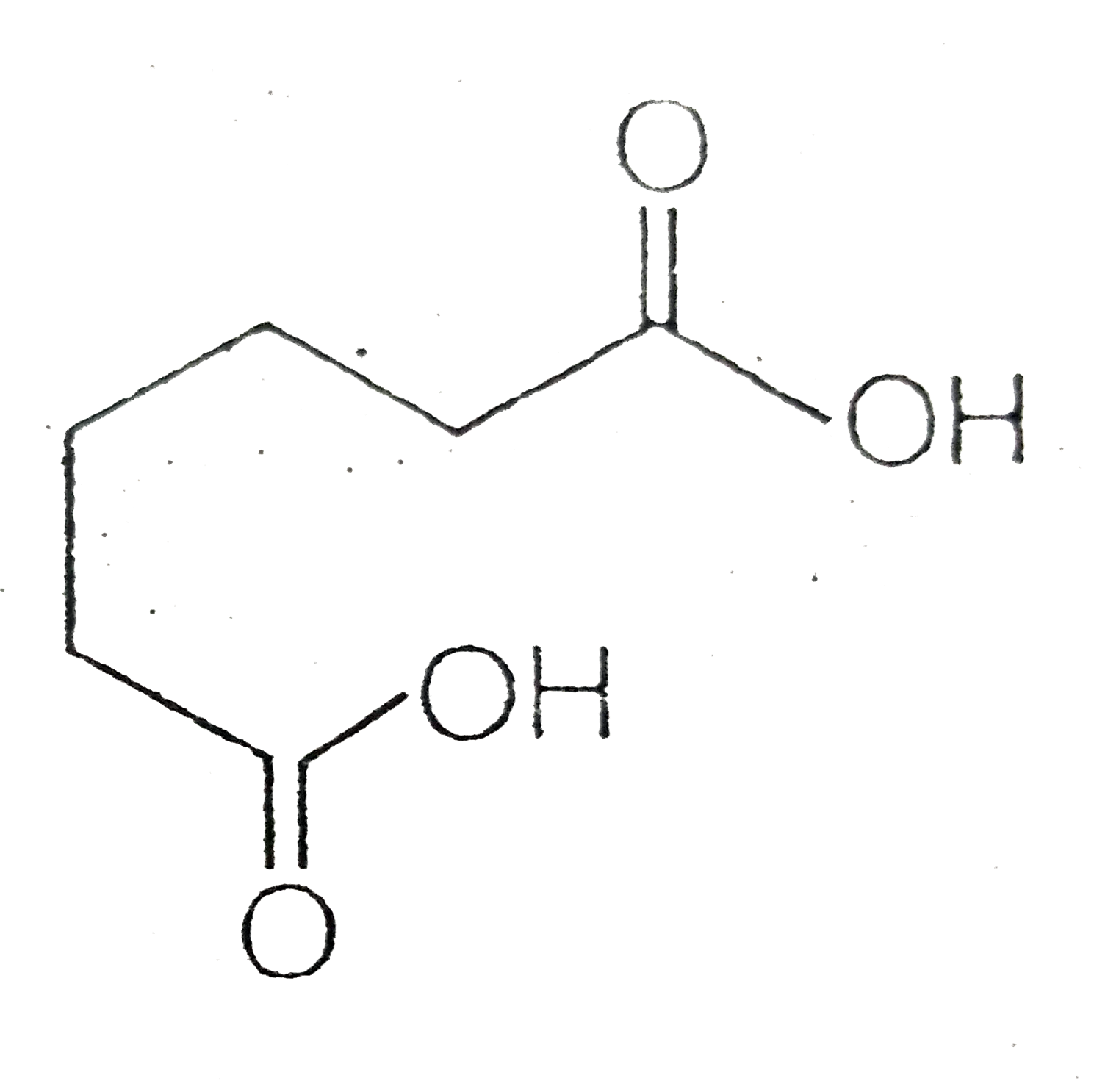
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment SECTION - E Assertion - Reason Type Questions)|7 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION - F Matrix Match type Questions)|4 VideosALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment (SECTION -C Objective type questions more than one options are correct)|11 VideosALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Try Yourself|5 VideosAMINES
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH|Exercise Assignment Section -J (Aakash Challengers Questions)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE ENGLISH-ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS -Assignment (SECTION -D Linked Comprehension type Questions)
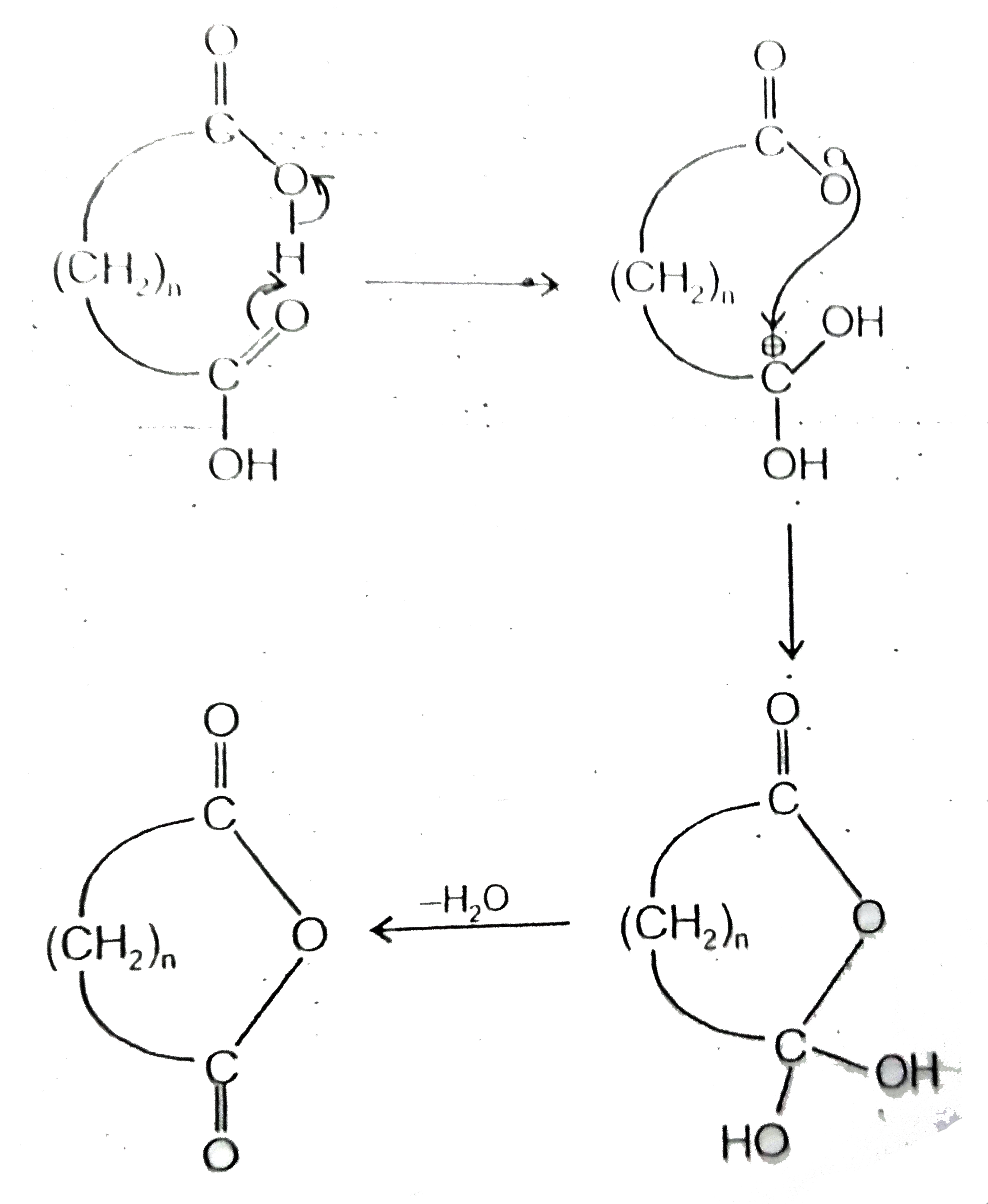
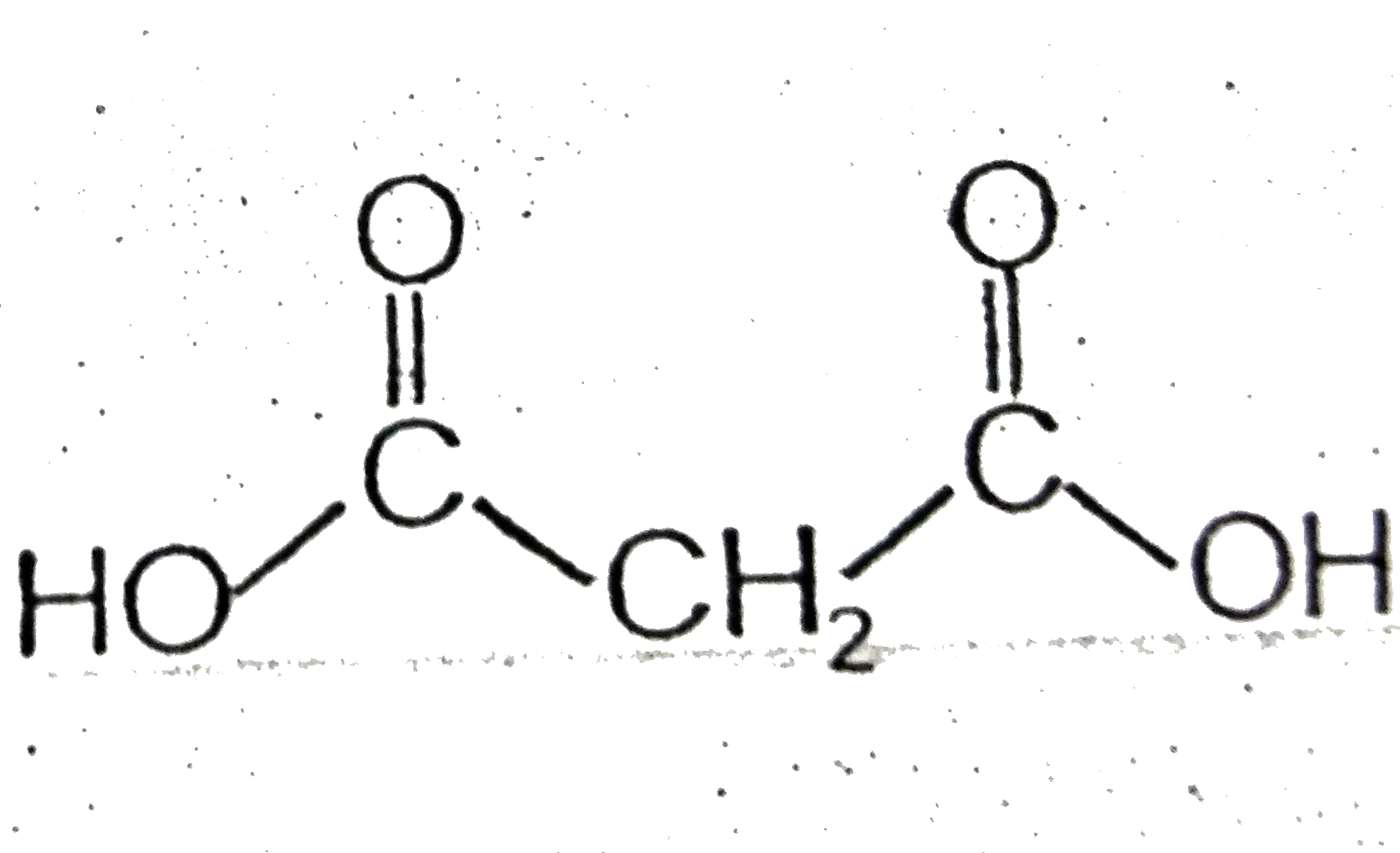
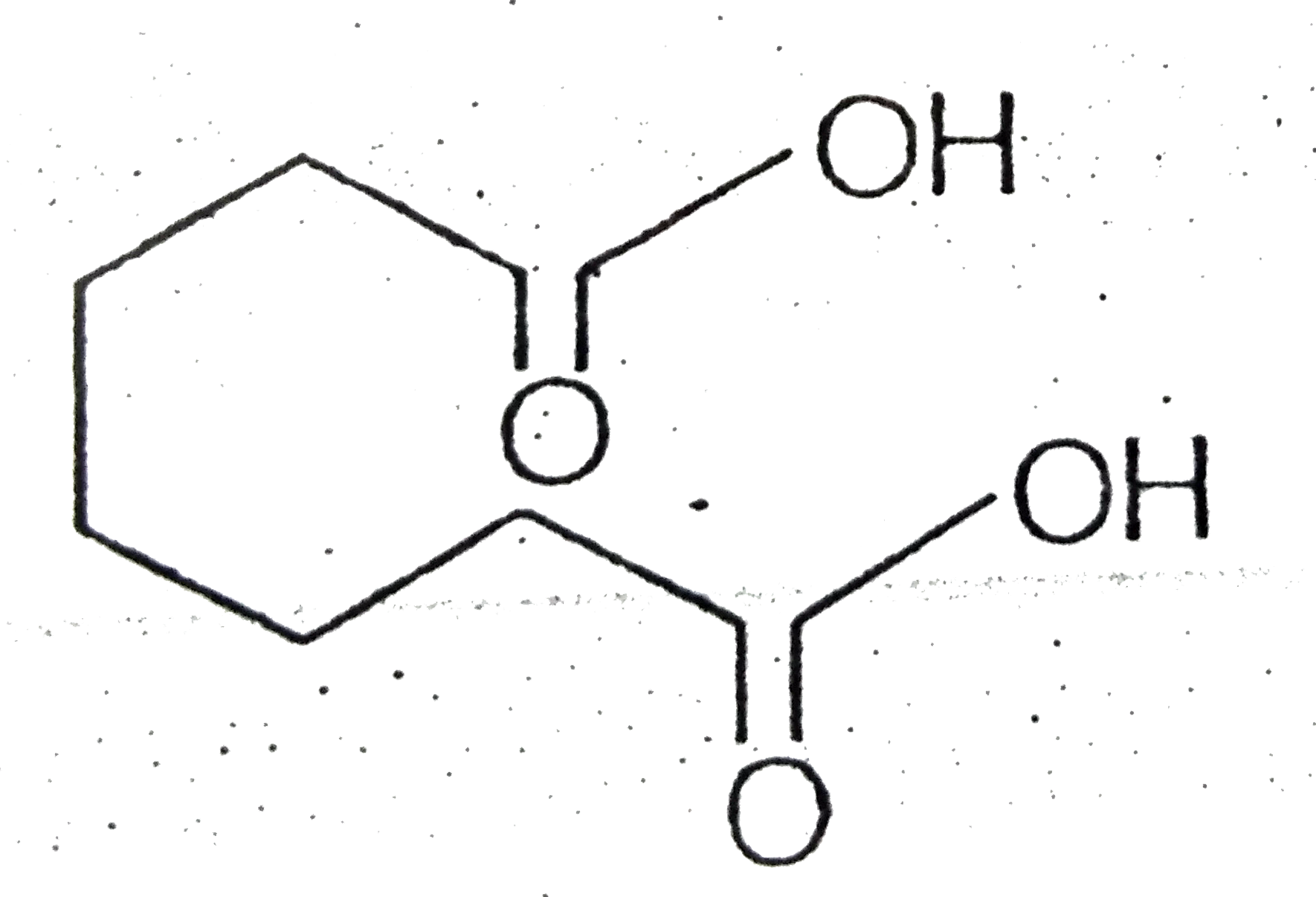
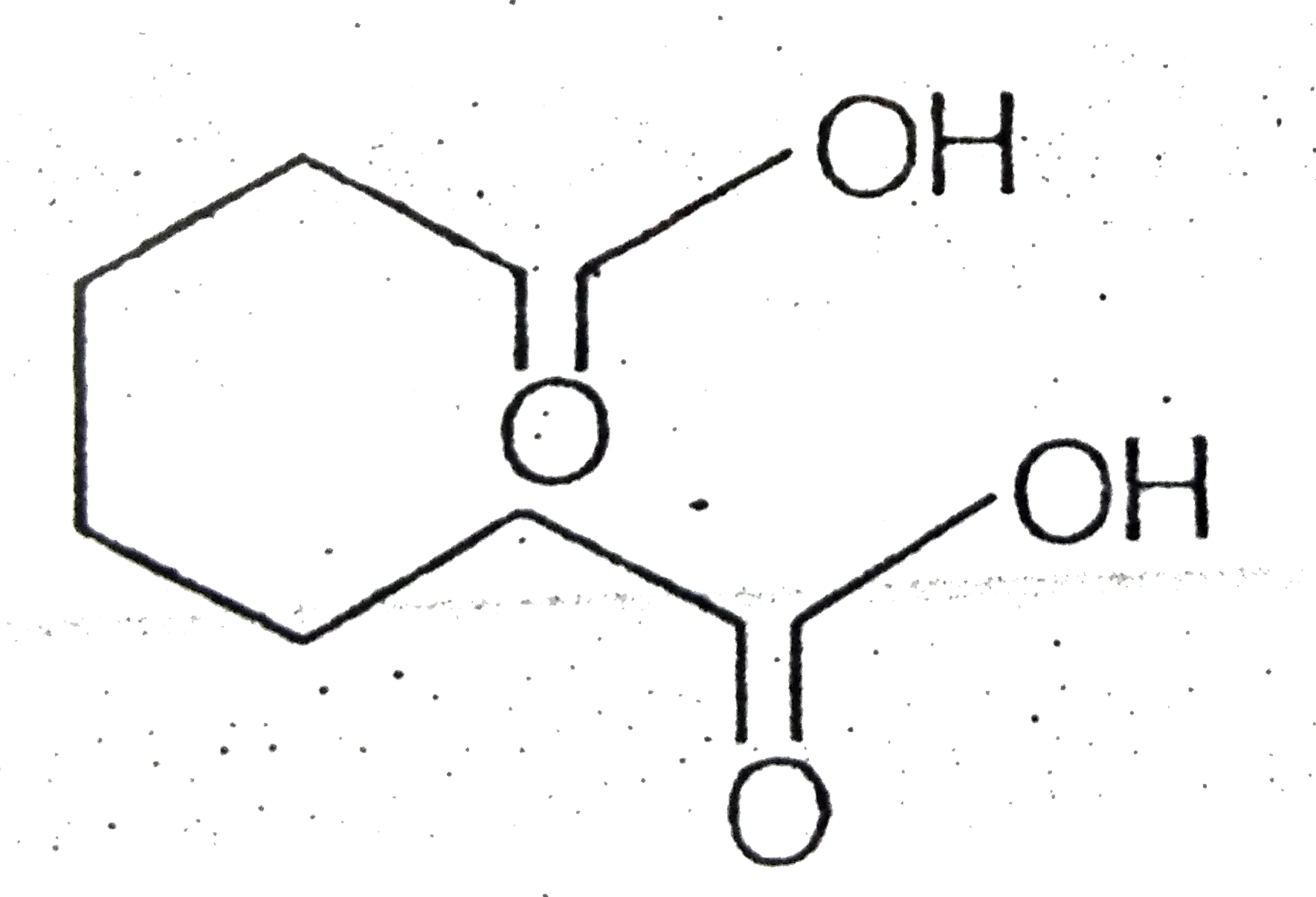
- Certain dicarboxylic acids spontaneously eliminate water when heated ...
Text Solution
|
- Certain dicarboxylic acids spontaneously eliminate water when heated ...
Text Solution
|
- Certain dicarboxylic acids spontaneously eliminate water when heated ...
Text Solution
|
- Both carbonyl compounds and acid derivatives though they contain grou...
Text Solution
|
- Both carbonyl compounds and acid derivatives though they contain grou...
Text Solution
|
- Both carbonyl compounds and acid derivatives though they contain grou...
Text Solution
|