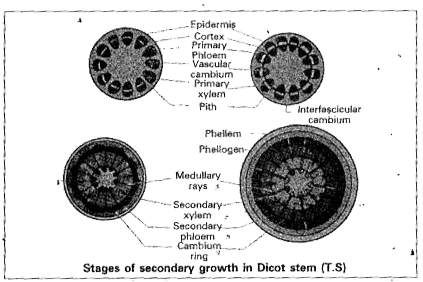
Formation of cambium ring : In the primary structure of dicto stem , the stele shows vascular bundles in the form of a ring . Each vascular bundle consists of camblum in between the xylem and phloem . This is called Inter fascicular cambium . In between the vascular bundles , there are medullary rays . From the cells of medullary rays intrafascicular cambium is formed . The inter fascicular and intrafasicular cambia fuse to form a continuous cambial ring called "vascular cambium ".
Activity of the vascular cambial ring : The cells of vascular cambium divide repeatedly by periclinal method and produce new cells on both the sides . The cells which are produced outside develop into secondary phloem and those produced to the inner side develop into secondary xylem (wood) . Generally more secondary xylem is produced than the secondary phloem . The secondary xylem consists of sieve tubes , companion cells , phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma .
In the cambium two types of initiating cells are found . They are 1. Fusiform initials and 2. Ray initials . The fusiform initials give rise to the secondary xylem and the secondary phloem . The ray initials produce phloem rays ( best ,rays ) to the outside and xylem rays (wood rays ) to the inside .They are helpful in lateral conduction and storage . They are called secondary medullary rays .
Annual rings : In temperate regions and cold regions the activity of the Cambium is influenced by the seasonal variations .During the faourable season , i.e ., in spring , when more leaves and flowers are formed , the plant requires large amounts of water and mineral salts , Hence the wood formed in ths period shows more number of xylem vessels with wider lumens . This is known as spring wood or early wood. The colour of this wood is light during the unfavourable season ie., in autumn , the plants are less active and do not require more water and mineral salts . Hence wood produced in the period shows less number of xylem vessels with narrow lumens . This is known as Autumn wood or late wood. It is dark coloured . In this way two types of secondary xylem (wood) are produced in one year . They appear in the form of dark and light coloured circles alternatly in a mature tree trunk . These are called Annual rings or growth rings or seasonal rings .
By counting the number of annual rings , the approximate age of trees can be estimated . This branch of science is known as "dendrochronology or growth ring analysis ". For example the age of sequoid dendrom , presently growing in America , is estimated to be about 3500 years . In tropical countries like India , annual rings do not appear clearly , as the seasonal variations are not sharp . hence these are called growth marks .
Heart wood and sapwood : With the increase in the age of the tree , the wood undergoes a number of physical and chemical changes . The older wood gradually loses water and stores food substances and becomes infiliterated with various organic compounds such as oils , gums , resins , tannins , colouring agents and aromatic substances . Hence the order xylem present in the centre appears dark in colour. This is called heart wood or duramen.
It is very hard higly durable .Heart wood cannot conduct water and salts because of the growth of tyloses in the lumens of xylem vessels . The heart wood gives mechanical strength to the tree.
The newly formed secondary xylem is found in the peripheral part of the tree trunk . This is called sapwood or alburnum . It is light in colour and is active in conducting water , mineral salts and storage of food materials .As time passes on , the sap wood gradually changes into heart wood. hence the sap wood remains uniformly thick .
Periderm : As the secondary xylem and secondary phloem are formed inside the stele , a pressure exerted on the epidermis , causing its rupture . Mea while a secondary protective layer formed the middle or inner part of the cortex its rupture . Mean while a secondary protective layer formed from the middle or inner part of the cortex become meristematic and acts as phellogen or cork cambium . These cells divide pericllinaly and cuts of new cells towards outside called cork or phellem and towards inside called secondary cortex or phelloderm . The phellogen , phellem and phelloderm together constitute periderm .
At certain regions , the phellogen cuts off closely arranged parenchymatous cells on the outer side instead of cork cells , called complementary cells . These cells soon rupture the epidermis forming a lens shaped openings called lenticels . They permit the exchange of gases betweery the outer atmosphere and the internal tissues .
.
 .
.